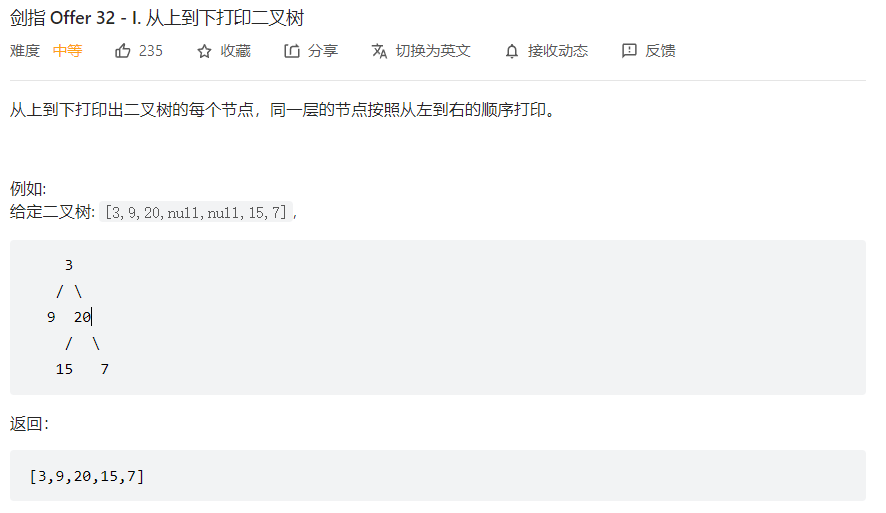
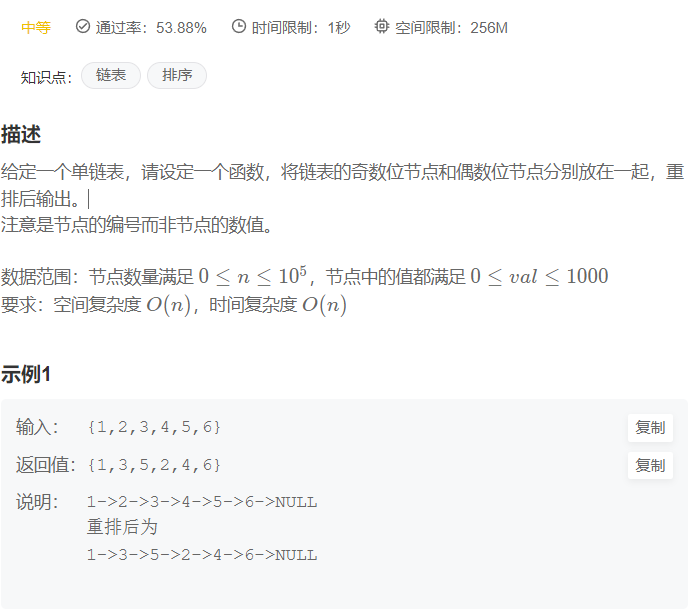
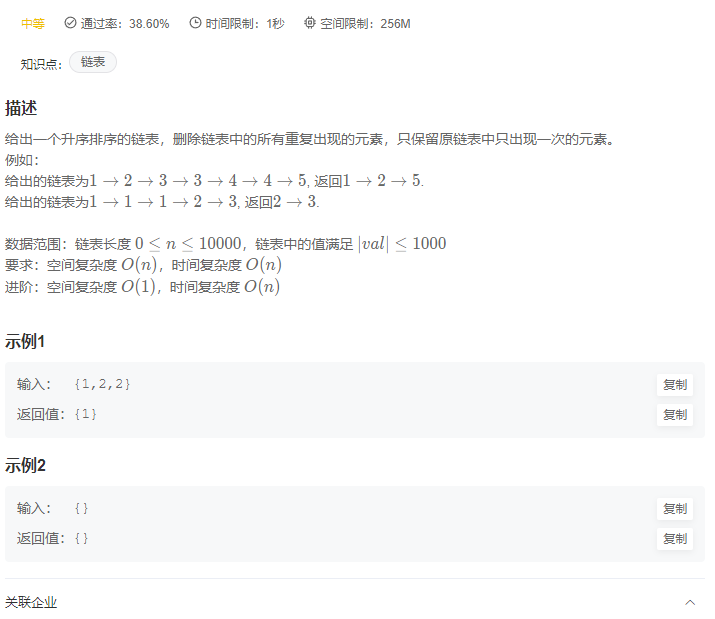
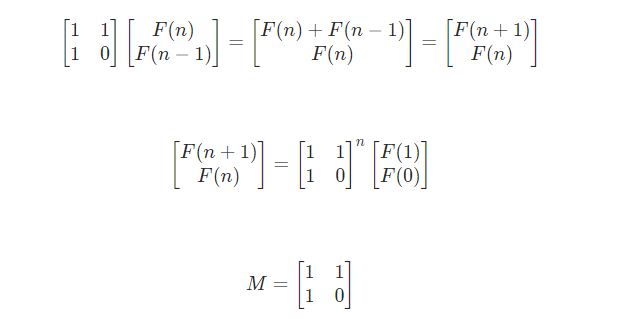给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出 和为目标值 target 的那 两个 整数,并返回它们的数组下标。
你可以假设每种输入只会对应一个答案。但是,数组中同一个元素在答案里不能重复出现。
你可以按任意顺序返回答案。
遍历nums中的元素num,num索引为i,判定target-num这个元素是否在nums[i+1,len(nums)],在则成功
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 class Solution : def twoSum (self, nums: List [int ], target: int ) -> List [int ]: result = [] for i in range (len (nums)): flag = target - nums[i] if (flag in nums[i+1 :len (nums)]): result.append(i) result.append(nums.index(flag,i+1 )) break return result
C语言
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 int * twoSum (int * nums, int numsSize, int target,int * returnSize) int flag = 0 ; int * returnArray = (int *)malloc (0x8 ); for (int i = 0 ; i < numsSize ; i++){ flag = target - nums[i]; for (int j = i+1 ; j < numsSize ; j++){ if (flag == nums[j]){ returnArray[0 ] = i; returnArray[1 ] = j; *returnSize=2 ; return returnArray; } } } return returnArray; }
挨个计算其模10的余数,打造回文数,判断与原数是否相等
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 bool isPalindrome (int x) if (x < 0 ){ return false ; } int num = x; long int cur = 0 ; while ( num != 0 ){ cur = cur*10 + num%10 ; num /= 10 ; } if (cur == x){ return true ; }else { return false ; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 char * longestCommonPrefix (char ** strs, int strsSize) if (strsSize == 0 ){ return "" ; } for (int j = 0 ; j < strsSize ; j ++){ if (sizeof (strs[j]) == 0 ){ return "" ; } } char * ans = strs[0 ]; char * com = malloc (0x200 ); int flag = 0 ; int len = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < sizeof (ans); i ++){ flag = 0 ; for (int j = 0 ; j < strsSize ; j ++){ if (ans[i] == strs[j][i]){ flag += 1 ; } else { break ; } } if (flag == strsSize){ continue ; } else { if (i == 0 ){ return "" ; } len = flag; break ; } } ans[len] = '\x00' ; return ans; }
进位计算,通过carry = sum / 10;来获取进位,sum = sum % 10;获取进位之后的值,然后用头节点依次串联起来,注意写的时候不要用局部变量当作返回结点,而是再分配一块内存来当作返回结点变量,不然会出错,可能是局部变量被覆盖之类的吧。
画解算法:2. 两数相加 - 两数相加 - 力扣(LeetCode)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 struct ListNode* addTwoNumbers (struct ListNode* l1, struct ListNode* l2) { struct ListNode * headNode =malloc (0x10 ); struct ListNode * curNode = int carry = 0 ; int sum = 0 ; while (l1 != NULL || l2 != NULL ) { int x = l1 == NULL ? 0 : l1->val; int y = l2 == NULL ? 0 : l2->val; sum = x + y + carry; carry = sum / 10 ; sum = sum % 10 ; curNode->next = (struct ListNode*) malloc (0x10 ); curNode->next->val = sum; curNode->next->next = NULL ; curNode = curNode->next; if (l1 != NULL ) l1 = l1->next; if (l2 != NULL ) l2 = l2->next; } if (carry == 1 ){ curNode->next = (struct ListNode*)malloc (0x10 ); curNode->next->val = carry; curNode->next->next = NULL ; } return headNode->next; }
自动机
依据每个状态进行转换,即确定所有状态,已经该状态的下个状态都有什么,这里就是如下所示的表格
空格
符号+/-
数字
其他符号
start
start
signed
in_number
end
signed
end
end
in_number
end
in_number
end
end
in_number
end
end
end
end
end
end
同时编程时设定
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 INT_MAX = 2 ** 31 - 1 INT_MIN = -2 ** 31 class Automaton : def __init__ (self ): self.state = 'start' self.sign = 1 self.ans = 0 self.table = { 'start' : ['start' , 'signed' , 'in_number' , 'end' ], 'signed' : ['end' , 'end' , 'in_number' , 'end' ], 'in_number' : ['end' , 'end' , 'in_number' , 'end' ], 'end' : ['end' , 'end' , 'end' , 'end' ], } def get_col (self, c ): if c.isspace(): return 0 if c == '+' or c == '-' : return 1 if c.isdigit(): return 2 return 3 def get (self, c ): self.state = self.table[self.state][self.get_col(c)] if self.state == 'in_number' : self.ans = self.ans * 10 + int (c) self.ans = min (self.ans, INT_MAX) if self.sign == 1 else min (self.ans, -INT_MIN) elif self.state == 'signed' : self.sign = 1 if c == '+' else -1 class Solution : def myAtoi (self, str : str ) -> int : automaton = Automaton() for c in str : automaton.get(c) return automaton.sign * automaton.ans
首先明确一个字符串,如果首尾两个字符相同,并且去掉这两个字符后的字符串还是回文字符串,那么这个字符串即为回文字符串。
abcba -> 去掉首尾aa -> bcb还是回文字符串,那么该字符串abcba即为回文字符串,这样就可以由大化小。
首先定义一个二维数组状态dp[i][j]即为str[i:j],若其值dp[i][j]为True,则代表子字符串str[i:j]为回文字符串。然后确定最开始的状态表,即最小的元素dp[i][i]
i\j
0
1
2
..
n
0
True
1
True
2
True
..
True
n
True
一个字符的子字符串一定为True,然后依据这个来判断外面的字符串是否为回文字符串。
由上可得,对应子字符串str[i:j]为回文字符串的必要条件为字符串str[i+1:j-1]为回文字符串,那么即可从小状态dp[i+1][j-1]赋值给大状态dp[i][j]
1 2 if (str [i] == str [j]): dp[i][j] = dp[i+1 ][j-1 ]
那么定义完成边界之后,就可以进行相关代码编写了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 myStr = "cbdsgfsdaadsas" myLen = len (myStr) dp = [[False ] * myLen for _ in range (myLen)] max_len = 1 begin = 0 for i in range (myLen): dp[i][i] = True for L in range (2 ,myLen + 1 ): for i in range (myLen): j = i + L - 1 if ( j >= myLen): break if (myStr[i] != myStr[j]): dp[i][j] = False else : if j-i < 3 : dp[i][j] = True else : dp[i][j] = dp[i+1 ][j-1 ] if (dp[i][j] and L > max_len): max_len = L begin = i print (myStr[begin:begin+max_len])
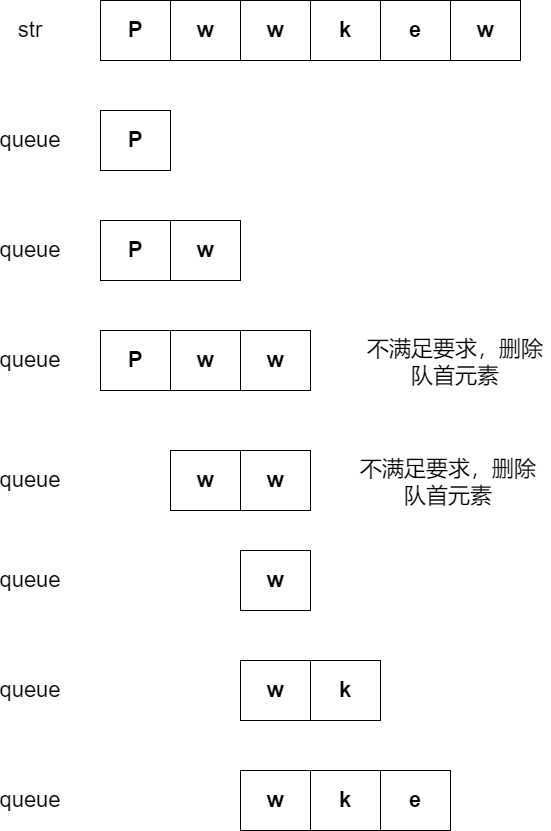
比如一个字符串str为pwwkew,首先从str[0]开始创建一个队列queue,其中元素为str[0]
将str[1]加入队列,满足无重复要求
之后将str[2]加入队列,发现不满足要求,记录此时的字符串长度为L,记下起始位置i并且和max_len对比取大值。
这时将队首元素str[0]移出队列,发现还是不满足要求,再将新的队首元素str[1]移出队列,发现满足要求了,接着循环
将str[3]加入队列,满足要求,依次循环
每一步大概如下
在加入队列不满足要求的时候记录此时的其实位置i和字符串长度L来取值比较即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution public int lengthOfLongestSubstring (String s) Set<Character> queue = new HashSet<Character>(); int n = s.length(); int rightPoint = 0 , max_len = 0 ; int L = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++){ while ( (rightPoint < n) && !queue.contains(s.charAt(rightPoint))){ queue.add(s.charAt(rightPoint)); rightPoint++; } L = rightPoint-i; if (L > max_len){ max_len = L; } if (rightPoint < n -1 ){ if (i == 0 ){ queue.remove(s.charAt(0 )); }else { queue.remove(s.charAt(i)); } }else { return max_len; } } return max_len; } }
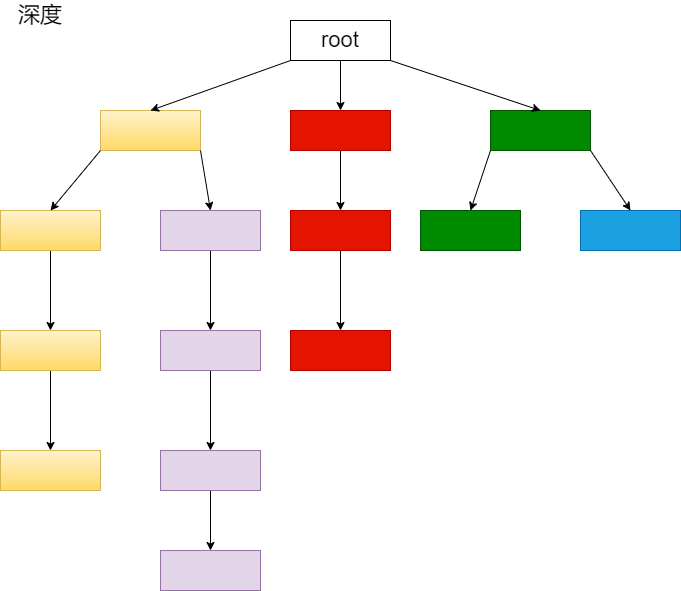
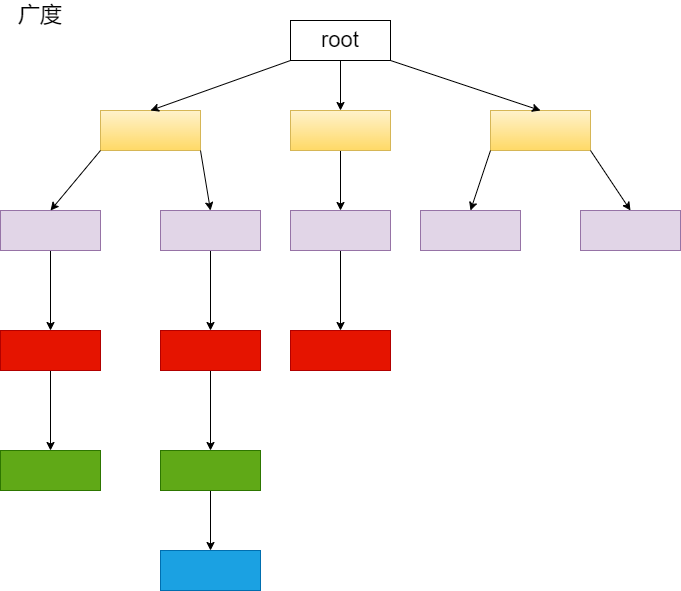
类似如下所示,遍历顺序为黄->紫->红->绿->蓝
即依据一个结点,从该结点的上下左右往外扩散遍历所有结点,遇到一个结点就进去遍历,核心思想是发现结点,先进再说。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution : def numIslands (self, grid: [[str ]] ) -> int : count = 0 def dfs (grid,i,j ): grid[i][j] = '0' if ((i-1 >= 0 ) and grid[i-1 ][j] == '1' ): dfs(grid,i-1 ,j) if ((i+1 < len (grid)) and grid[i+1 ][j] == '1' ): dfs(grid,i+1 ,j) if ((j-1 >= 0 ) and grid[i][j-1 ] == '1' ): dfs(grid,i,j-1 ) if ((j+1 < len (grid[0 ])) and grid[i][j+1 ] == '1' ): dfs(grid,i,j+1 ) for i in range (0 ,len (grid)): for j in range (0 ,len (grid[0 ])): if (grid[i][j] == '1' ): dfs(grid,i,j) count = count + 1 return count
类似如下所示,遍历顺序同样为黄->紫->红->绿->蓝,相当于是一层一层的
但是这样就需要用到一个队列,从一个结点出发的下一层都放到该队列尾部,然后从队首取结点,再遍历,将该结点的下一层也放入队列尾部,依次循环。
有点像将一个结点的出口点全面存储起来放到一个队列的最后一起进行遍历
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution : def numIslands (self, grid: [[str ]] ) -> int : count = 0 def bfs (grid,i,j ): queue = [[i,j]] while queue: [i,j] = queue.pop(0 ) if (grid[i][j] == '1' ): grid[i][j] = '0' if ((i-1 >= 0 ) and grid[i-1 ][j] == '1' ): queue.append([i-1 ,j]) if ((i+1 < len (grid)) and grid[i+1 ][j] == '1' ): queue.append([i+1 ,j]) if ((j-1 >= 0 ) and grid[i][j-1 ] == '1' ): queue.append([i,j-1 ]) if ((j+1 < len (grid[0 ])) and grid[i][j+1 ] == '1' ): queue.append([i,j+1 ]) for i in range (0 ,len (grid)): for j in range (0 ,len (grid[0 ])): if (grid[i][j] == '1' ): bfs(grid,i,j) count = count + 1 return count
贪心算法、双指针
确定两个指针从头尾开始,依次往中间收缩,由于是装水容量由短板决定,所以对于例子container[0:8]组成的容器来说,左指针对应高度小于右指针对应高度,所以右指针如果往左移动,其容量只会减少。那么我们就尝试将左指针往右移动,企图寻找更大的容器。
其证明感觉没见到几个讲的很清楚的。
这里需要明白一点,最大的容器左右边界之外如果还有边界,那么外面的边界的最大值一定比这个最大容器的短板更短,如果更长,那么挪过去之后,肯定容器更大了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution : def maxArea (self, height: List [int ] ) -> int : i = 0 res = 0 j = len (height)-1 while i < j: if (height[i] < height[j]): res = max (res,height[i]*(j-i)) i += 1 else : res = max (res,height[j] * (j-i)) j -= 1 return res
([)]
number
符号##/边界
right
right
down
down
down
left
left
left
up
up
up
right
由此写出自动机相关代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 class Automaton : def __init__ (self,matrix ): self.matrix = matrix self.state = 'right' self.i = 0 self.j = -1 self.myList = [] self.table = { 'right' : ['right' , 'down' ], 'down' : ['down' , 'left' ], 'left' : ['left' , 'up' ], 'up' : ['up' , 'right' ], } def get_col (self,i,j ): if j >= len (self.matrix[0 ]) or (i >= len (self.matrix)) or (j < 0 ) or (i < 0 ): return 1 if self.matrix[i][j] == '#' : return 1 if isinstance (self.matrix[i][j],int ): return 0 def nextState (self,i,j ): if (self.state == "right" ): j += 1 if (self.state == "down" ): i += 1 if (self.state == "left" ): j -= 1 if (self.state == "up" ): i -= 1 self.state = self.table[self.state][self.get_col(i,j)] def start (self ): for i in range (len (self.matrix)*len (self.matrix[0 ])): self.nextState(self.i,self.j) if (self.state == "right" ): self.j += 1 if (self.state == "down" ): self.i += 1 if (self.state == "left" ): self.j -= 1 if (self.state == "up" ): self.i -= 1 self.myList.append(self.matrix[self.i][self.j]) self.matrix[self.i][self.j] = '#' class Solution : def spiralOrder (self, matrix: List [List [int ]] ) -> List [int ]: test = Automaton(matrix) test.start() return test.myList
另一个方法是获取依照层进行遍历,当遍历完一层之后,去掉外层,然后再遍历。
(top,left)、(top,right)、(bottom,left)、(bottom,right)为矩阵边界点,每次遍历完一层之后,对相应的结点数据进行增减。
明确一个公式
deepth(root) = max(deepth(root.rigth),deepth(root.left)) + 1
即每一个二叉树的深度等于其左子树和右子树中的最大深度再加上根节点,然后其左子树和右子树又可以被当作一个新的二叉树来进行获得其深度,类似动态规划的递归写法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class Solution : def maxDepth (self, root: Optional [TreeNode] ) -> int : if (root is None ): return 0 else : return max (self.maxDepth(root.right),self.maxDepth(root.left)) + 1
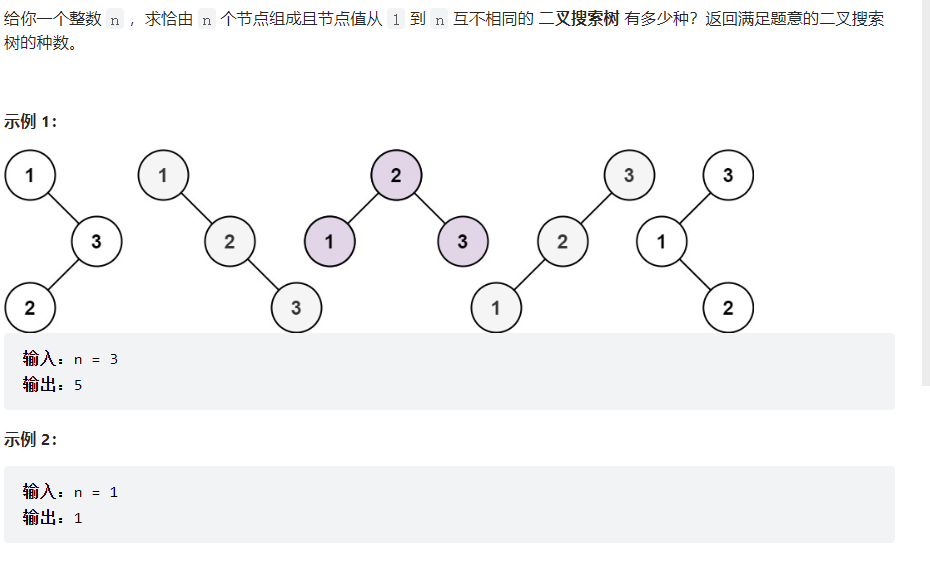
依次类推,最开始时需要的元素为G(0)和G(1)可以推导得出其他所有的G(n),依据卡特兰公式即可得到状态转移方程
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 class Solution : def numTrees (self, n: int ) -> int : dp = [0 ]*(n+1 ) dp[0 ] = 1 dp[1 ] = 1 for i in range (2 ,n+1 ): for j in range (0 ,i): dp[i] += dp[j]*dp[i-1 -j] return dp[n]
1 int array [10 ] = {3 ,4 ,5 ,2 ,1 ,3 ,4 ,2 ,2 ,1 ,};
构建大顶堆,首先依据顺序排列成二叉完全树
然后从idx最大的非叶子结点的子树开始,这里就是idx=4,计算方法为一个循环来大概判断
然后获取取左右子树的根结点,二叉树基本原理
1 2 int leftIdx = i * 2 + 1 ;int rightIdx = i * 2 + 2 ;
之后进行判断排序,获取最大的进行交换调整,将大的上移,然后将下移的结点作为一个二叉树根节点继续调整,依次循环
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 int maxIdx = rootIdx;if ( leftIdx < heapSize && array [leftIdx] > array [maxIdx]){ maxIdx = leftIdx; } if ( rightIdx < heapSize && array [rightIdx] > array [maxIdx]){ maxIdx = rightIdx; } if ( maxIdx != rootIdx){ int tmp = array [rootIdx]; array [rootIdx] = array [maxIdx]; array [maxIdx] = tmp; maxJustHeap(array ,maxIdx,heapSize); }
完整代码为
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 void maxJustHeap (int * array ,int rootIdx,int heapSize) int leftIdx = rootIdx * 2 + 1 ; int rightIdx = rootIdx * 2 + 2 ; int maxIdx = rootIdx; if ( leftIdx < heapSize && array [leftIdx] > array [maxIdx]){ maxIdx = leftIdx; } if ( rightIdx < heapSize && array [rightIdx] > array [maxIdx]){ maxIdx = rightIdx; } if ( maxIdx != rootIdx){ int tmp = array [rootIdx]; array [rootIdx] = array [maxIdx]; array [maxIdx] = tmp; maxJustHeap(array ,maxIdx,heapSize); } } void buildMaxHeap (int * array ,int heapSize) for (int i = heapSize/2 ; i >= 0 ; i--){ maxJustHeap(array ,i,heapSize); } } int main () int array [10 ] = {3 ,4 ,5 ,2 ,1 ,3 ,4 ,2 ,2 ,1 ,}; buildMaxHeap(array ,10 ); return 0 ; }
完整过程为
即可完成最终调整
之后删除掉K-1个堆顶元素剩下的堆,即可得到第K个大小的元素。但是堆的删除操作也有点复杂,参照(46条消息) 【数据结构】【堆】堆的建立、插入和删除_西西敏的博客-CSDN博客_堆的建立
为了将这个节点删除后的空位填补上,首先要将本堆中最后一个元素的值(假设为value)移动到此位置,然后在被删位置处,用此位置当前的值value和此处的父节点、子节点去比较,如果它与父节点的关系破坏了最大(小)堆,则递归调用shiftUp()来修复;如果它与子节点的关系破坏了最大(小)堆,则递归调用shiftDown()来修复。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 void maxJustHeap (int * array ,int rootIdx,int heapSize) int leftIdx = rootIdx * 2 + 1 ; int rightIdx = rootIdx * 2 + 2 ; int maxIdx = rootIdx; if ( leftIdx < heapSize && array [leftIdx] > array [maxIdx]){ maxIdx = leftIdx; } if ( rightIdx < heapSize && array [rightIdx] > array [maxIdx]){ maxIdx = rightIdx; } if ( maxIdx != rootIdx){ int tmp = array [rootIdx]; array [rootIdx] = array [maxIdx]; array [maxIdx] = tmp; maxJustHeap(array ,maxIdx,heapSize); } } void buildMaxHeap (int * array ,int heapSize) for (int i = heapSize/2 ; i >= 0 ; i--){ maxJustHeap(array ,i,heapSize); } } int findKthLargest (int * nums, int numsSize, int k) buildMaxHeap(nums,numsSize); int heapSize = numsSize; for (int i = 0 ; i < k - 1 ; i ++){ nums[0 ] = nums[heapSize-1 ]; heapSize -= 1 ; maxJustHeap(nums,0 ,heapSize); } return nums[0 ]; }
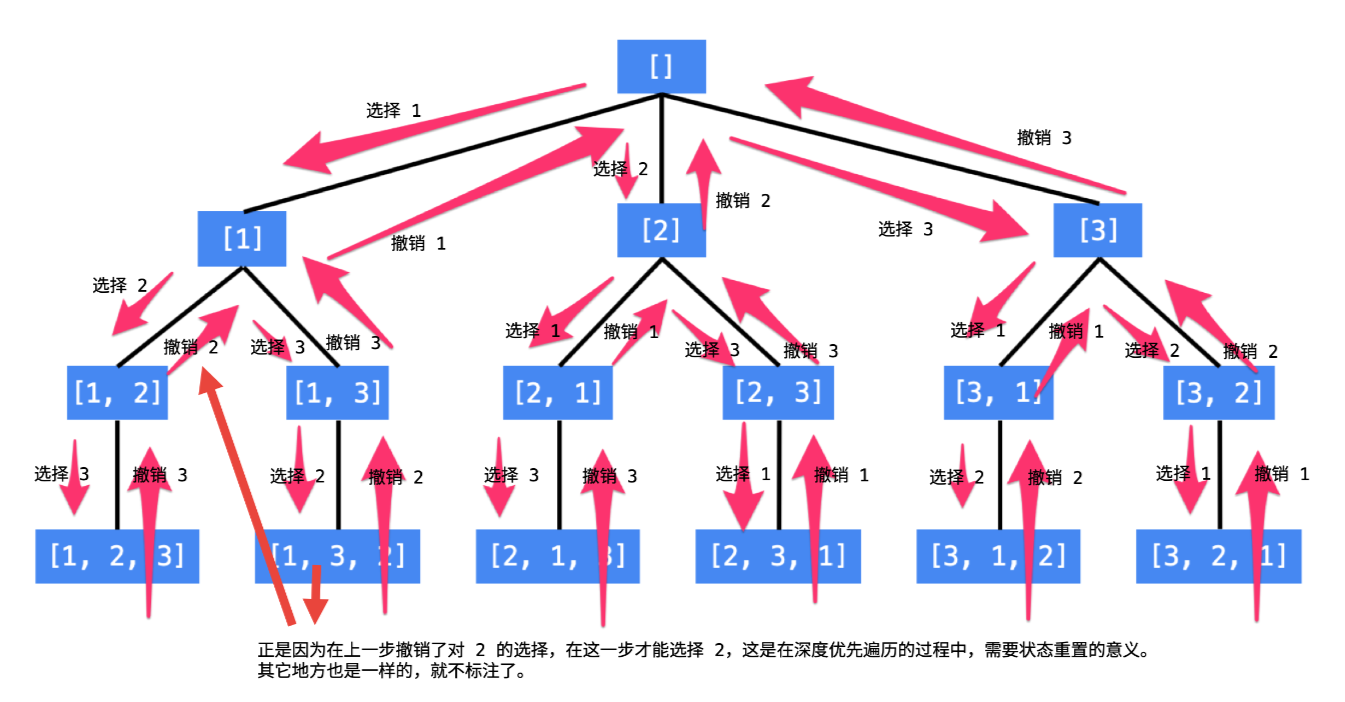
使用回溯算法解决
参考:回溯算法入门级详解 + 练习(持续更新) - 全排列 - 力扣(LeetCode)
参考图解为
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution : def permute (self, nums: List [int ] ) -> List [List [int ]]: res = [] def back (nums,tmp ): if (not nums): res.append(tmp) return for i in range (len (nums)): tmpNums = nums[:i] + nums[i+1 :] tmpTmp = tmp + [nums[i]] back(tmpNums,tmpTmp) back(nums,[]) return res
即每次进入回溯时,进入下一轮的可遍历的数组都是上一轮的数组减去当前要进入tmp剩下的数组,在C上可以使用一个int数组vis来代替是否被遍历到了。
直接归并然后返回中位数的时间复杂度为O(m+n)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class Solution : def findMedianSortedArrays (self, nums1: List [int ], nums2: List [int ] ) -> float : result = [] i = 0 j = 0 nums1Len = len (nums1) nums2Len = len (nums2) while (True ): if (nums1Len == 0 ): result += nums2 break if (nums2Len == 0 ): result += nums1 break if (nums1[i] < nums2[j]): result.append(nums1[i]) i += 1 if (i == nums1Len): result += nums2[j:] break else : result.append(nums2[j]) j += 1 if (j == nums2Len): result += nums1[i:] break resultLen = len (result) if (resultLen%2 == 0 ): return (result[int (resultLen/2 )-1 ] + result[int (resultLen/2 )])/2 else : return result[int (resultLen/2 )]
即寻找两个有序数组排序之后的第k个数,假定如下
1 2 k = (len(a) + len(b))/2 len(a) + len(b)为奇数 k为中位数索引 k = (len(a) + len(b))/2 + 1 len(a) + len(b)为偶数 k为中位数索引+0.5
然后尝试比较a[k/2-1]和b[k/2-1]
a[k/2-1] > b[k/2-1]时,比b[k/2-1]小或等于的最多只有(k/2-1)*2=k-2个数,那么该数b[k/2-1]必定不可能是中位数,那么排除b[0:k/2-1]
a[k/2-1] < b[k/2-1]时,同理,排除a[0:k/2-1]
a[k/2-1] = b[k/2-1]时,也同理,排除a[0:k/2-1]和b[0:k-2/1]
时间复杂度为O(logn),那么就用二分查找
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 from typing import List class Solution : def search (self,nums,left,right,target ): if (left > right): return None mid = (left + right)//2 if (nums[mid] < target): left = mid + 1 idx = self.search(nums,left,right,target) elif (nums[mid] > target): right = mid - 1 idx = self.search(nums,left,right,target) elif (nums[mid] == target): return mid return idx def searchRange (self, nums: List [int ], target: int ) -> List [int ]: res = [] idx = self.search(nums,0 ,len (nums)-1 ,target) if (idx == None ): res = [-1 ,-1 ] else : left = idx - 1 right = idx + 1 while (left >= 0 and nums[left] == target): left -= 1 while (right < len (nums) and nums[right] == target): right += 1 res = [left+1 ,right-1 ] return res
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 class LRUCache class DLinkedNode private int key; private int value; private DLinkedNode next; private DLinkedNode prev; public DLinkedNode () public DLinkedNode (int _key, int _value) this .key = _key; this .value = _value; } } private int size; private int capacity; private Map<Integer,DLinkedNode> cache; private DLinkedNode head; private DLinkedNode tail; public LRUCache (int capacity) this .size = 0 ; this .capacity = capacity; this .head = new DLinkedNode(); this .tail = new DLinkedNode(); this .head.next = this .tail; this .tail.prev = this .head; this .cache = new HashMap<Integer,DLinkedNode>(); } public void put (int key,int value) DLinkedNode node = this .cache.get(key); if (node == null ){ DLinkedNode newNode = new DLinkedNode(key,value); addToHead(newNode); this .cache.put(key,newNode); size ++; if (size > capacity){ DLinkedNode needRmNode = this .tail.prev; removeNode(needRmNode); this .cache.remove(needRmNode.key); size --; } }else { node.value = value; moveToHead(node); } } public int get (int key) DLinkedNode node = this .cache.get(key); if (node == null ){ return -1 ; }else { moveToHead(node); return node.value; } } public void addToHead (DLinkedNode node) node.next = this .head.next; node.prev = this .head; this .head.next.prev = node; this .head.next = node; } public void removeNode (DLinkedNode node) node.prev.next = node.next; node.next.prev = node.prev; } public void moveToHead (DLinkedNode node) removeNode(node); addToHead(node); } }
利用栈匹配即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution : def isValid (self, s: str ) -> bool : dict = { "(" :")" , "[" :"]" , "{" :"}" } stack = [] for chr in s: if (chr in dict ): stack.append(chr ) else : if (len (stack) > 0 ): top = stack.pop() if (dict [top] == chr ): continue else : return False else : return False if (len (stack) == 0 ): return True else : return False
一次遍历,找出当前阶段价格最小的一天然后进行计算利益替换最大利益
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 class Solution : def maxProfit (self, prices: List [int ] ) -> int : maxProfit = 0 minDay = 0 for i in range (0 ,len (prices)): if (prices[i] < prices[minDay]): minDay = i elif (prices[i] - prices[minDay] > maxProfit): maxProfit = prices[i] - prices[minDay] return maxProfit
快排加双指针
定位一个位置,然后一步步逼近
参考:三数之和(排序+双指针,易懂图解) - 三数之和 - 力扣(LeetCode)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 class Solution : def threeSum (self, nums: [int ] ) -> [[int ]]: self.quickStart(nums) res = [] for k in range (0 ,len (nums)-2 ): if (nums[k] > 0 ): break if (k > 0 and nums[k-1 ]==nums[k]): continue j = len (nums) - 1 i = k + 1 while (i < j): s = nums[k] + nums[i] + nums[j] if (s < 0 ): i += 1 while (i < j and nums[i] == nums[i-1 ]): i += 1 elif (s > 0 ): j -= 1 while (i < j and nums[j] == nums[j+1 ]): j -= 1 else : res.append([nums[k],nums[i],nums[j]]) i += 1 j -= 1 while i < j and nums[i] == nums[i - 1 ]: i += 1 while i < j and nums[j] == nums[j + 1 ]: j -= 1 return res def partition (self,nums,low,high ): pivot_idx = random.randint(low,high) pivot = nums[pivot_idx] nums[low],nums[pivot_idx] = nums[pivot_idx],nums[low] left = low right = high while (left < right): while (left < right and pivot <= nums[right]): right -= 1 nums[left] = nums[right] while (left < right and pivot >= nums[left]): left += 1 nums[right] = nums[left] nums[left] = pivot return left def quickSort (self,nums,low,high ): if (low >= high): return mid = self.partition(nums,low,high) self.quickSort(nums,low,mid - 1 ) self.quickSort(nums,mid + 1 , high) def quickStart (self,nums ): self.quickSort(nums,0 ,len (nums)-1 )
计算所有表面积减去重叠表面积
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution : def surfaceArea (self, grid: List [List [int ]] ) -> int : full = 0 overlap = 0 myLen = len (grid[0 ]) for i in range (0 ,myLen): for j in range (0 ,myLen): leftOver, topOver, rightOver, downOver = 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 full += 1 * grid[i][j] * 4 + 1 *2 *(1 if grid[i][j] > 0 else 0 ) if (i - 1 >= 0 ): topOver = min (grid[i][j],grid[i-1 ][j])*1 if (j - 1 >= 0 ): leftOver = min (grid[i][j],grid[i][j-1 ])*1 if (i + 1 < myLen): downOver = min (grid[i][j],grid[i+1 ][j])*1 if (j + 1 < myLen): rightOver = min (grid[i][j],grid[i][j+1 ])*1 tmplap = leftOver + topOver + rightOver + downOver overlap += tmplap return full - overlap
深度优先搜索加缓存,保证不重复遍历
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 class Solution private int [][] direction = {{-1 ,0 },{1 ,0 },{0 ,-1 },{0 ,1 }}; private int rowLens; private int columnLens; public int longestIncreasingPath (int [][] matrix) int result = 0 ; this .rowLens = matrix.length; this .columnLens = matrix[0 ].length; int [][] mem = new int [rowLens][columnLens]; for (int row = 0 ; row < rowLens ; row++){ for (int column = 0 ; column < columnLens ; column++){ result = Math.max(result,dfs(matrix,mem,row,column)); } } return result; } public int dfs (int [][] matrix,int [][] mem,int row,int column) if (mem[row][column] > 0 ){ return mem[row][column]; } mem[row][column] += 1 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < this .direction.length ; i ++){ int newRow = row + this .direction[i][0 ]; int newColumn = column + this .direction[i][1 ]; if (0 <= newColumn && newColumn < this .columnLens && 0 <= newRow && newRow < this .rowLens && matrix[newRow][newColumn] > matrix[row][column]){ mem[row][column] = Math.max(mem[row][column],dfs(matrix,mem,newRow,newColumn) + 1 ); } } return mem[row][column]; } }
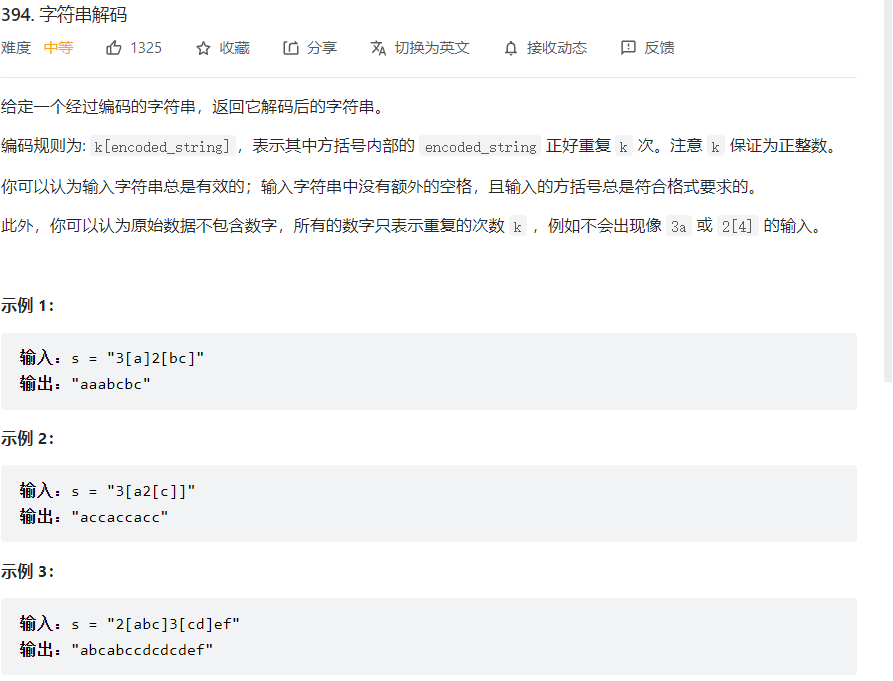
利用栈即可实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution : def decodeString (self, s: str ) -> str : res = "" stack = [] pushList = "0123456789[abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz" for i in s: tmp = "" if (i in pushList): stack.append(i) else : top = stack.pop() while (top != "[" ): tmp = top + tmp top = stack.pop() top = stack.pop() num = "" while (top != "" and ('0' <= top <= '9' )): num = top + num if (len (stack) > 0 ): top = stack.pop() else : break tmp = int (num) * tmp if (top != "" and (top < '0' or top > '9' )): stack.append(top) stack = stack + list (tmp) return res + "" .join(stack)
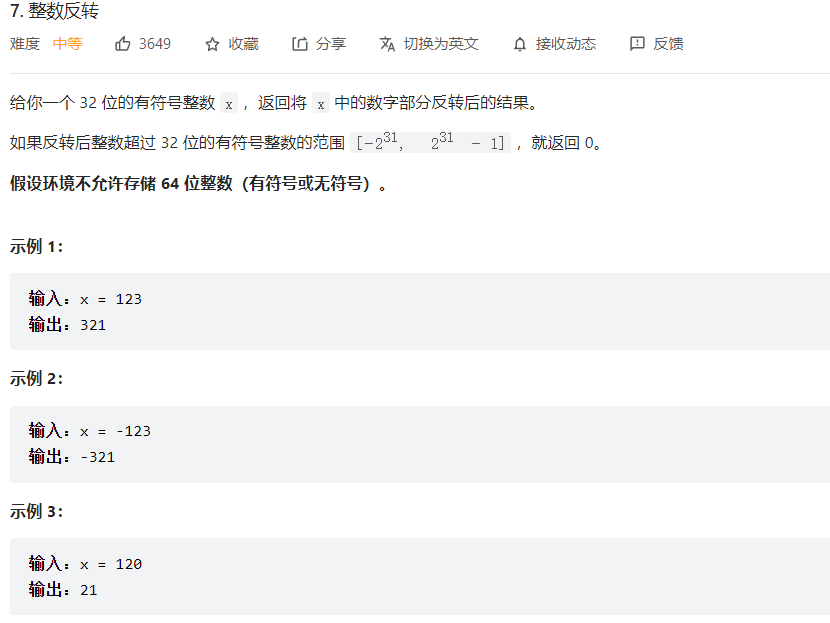
使用模加除即可解决,主要考虑溢出情况
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution public int reverse (int x) if (x == Integer.MIN_VALUE) return 0 ; int calcuTmp = 0 ; int signed = 0 ; if (x < 0 ) { signed = -1 ; } else if (x == 0 ) { return x; } else { signed = 1 ; } int tmp = signed * x; while (tmp != 0 ) { if (calcuTmp > Integer.MAX_VALUE/10 ){ return 0 ; } calcuTmp *= 10 ; calcuTmp += (tmp % 10 ); tmp = (tmp - (tmp % 10 )) / 10 ; } return signed * calcuTmp; } }
全排列问题基本都用回溯法解决,基本公式就是
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 def back (idx ): if (limitCondition): return for i in inputList: operate() back(idx+1 ) operate() back(0 )
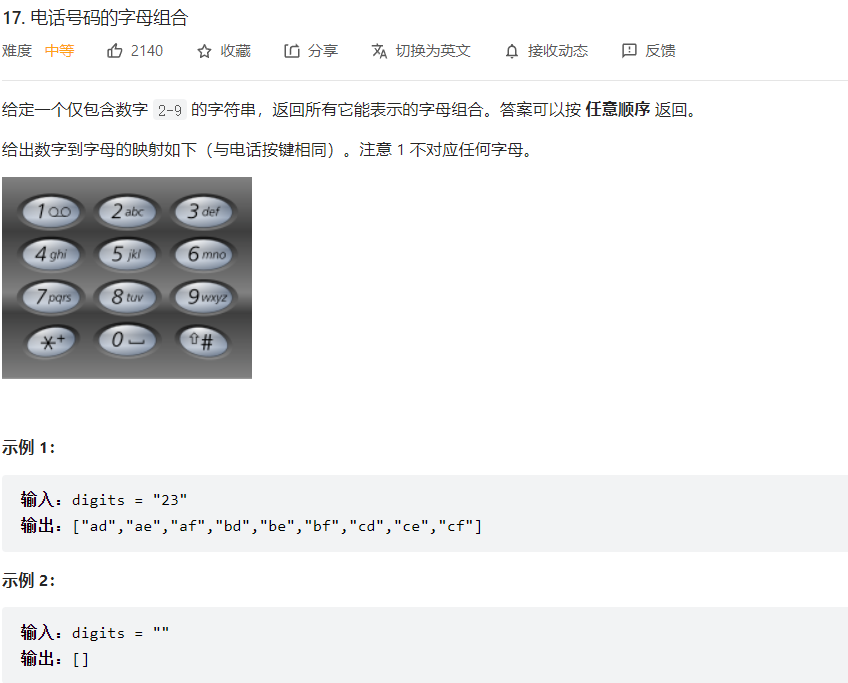
如下解决
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution : def letterCombinations (self, digits: str ) -> List [str ]: phoneMap = { "2" : "abc" , "3" : "def" , "4" : "ghi" , "5" : "jkl" , "6" : "mno" , "7" : "pqrs" , "8" : "tuv" , "9" : "wxyz" , } com = [] coms = [] def backTrace (idx ): if (idx == len (digits)): return digit = digits[idx] for letter in phoneMap[digit]: com.append(letter) backTrace(idx + 1 ) if (len (com) == len (digits)): coms.append("" .join(com)) com.pop() backTrace(0 ) return coms
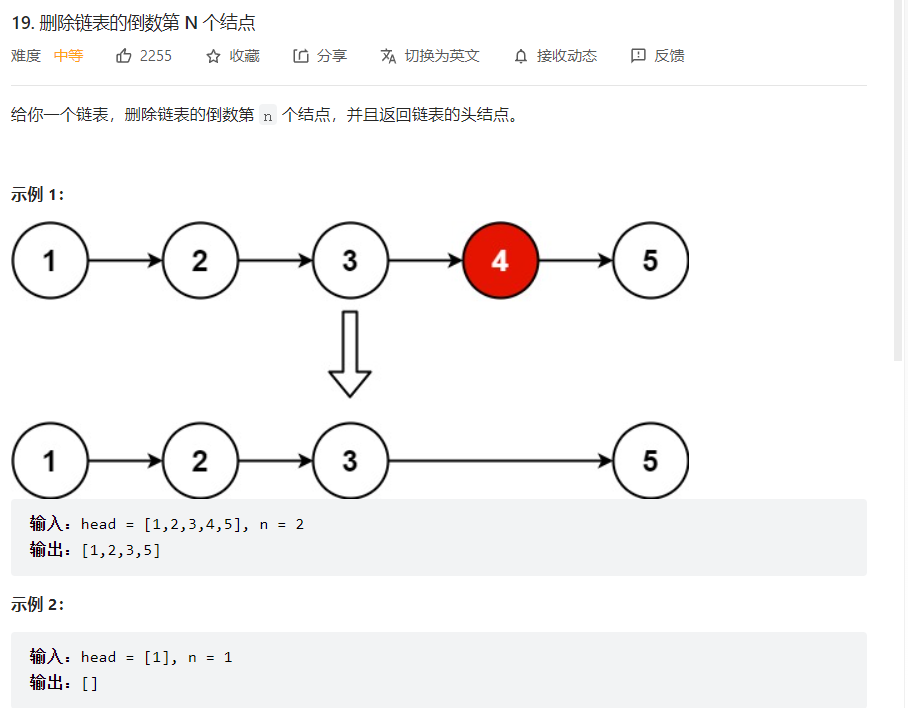
使用快慢指针
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution public ListNode removeNthFromEnd (ListNode head, int n) ListNode beHead = new ListNode(); beHead.next = head; ListNode fastPoint = beHead; ListNode slowPoint = beHead; while (n > 0 ){ fastPoint = fastPoint.next; n--; } while (fastPoint.next != null ){ slowPoint = slowPoint.next; fastPoint = fastPoint.next; } slowPoint.next = slowPoint.next.next; return beHead.next; } }
当然先一次遍历获取链表长度也可以。
或者使用栈来进行辅助,遍历一遍全部压入,然后弹出N个结点即可。
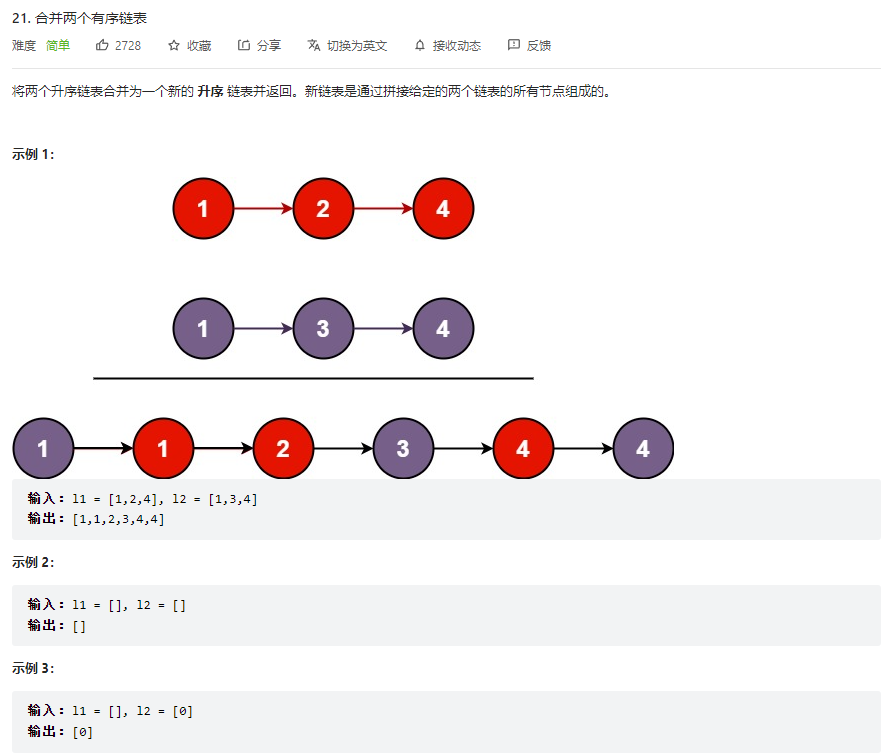
直接归并即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution public ListNode mergeTwoLists (ListNode list1, ListNode list2) ListNode newList = new ListNode(); ListNode originList = newList; while (list1 != null && list2 != null ){ while (list1 != null && list2 != null && list1.val <= list2.val){ newList.next = list1; newList = newList.next; list1 = list1.next; } while (list1 != null && list2 != null && list2.val <= list1.val ){ newList.next = list2; newList = newList.next; list2 = list2.next; } } if (list1 == null ){ newList.next = list2; }else { newList.next = list1; } return originList.next; } }
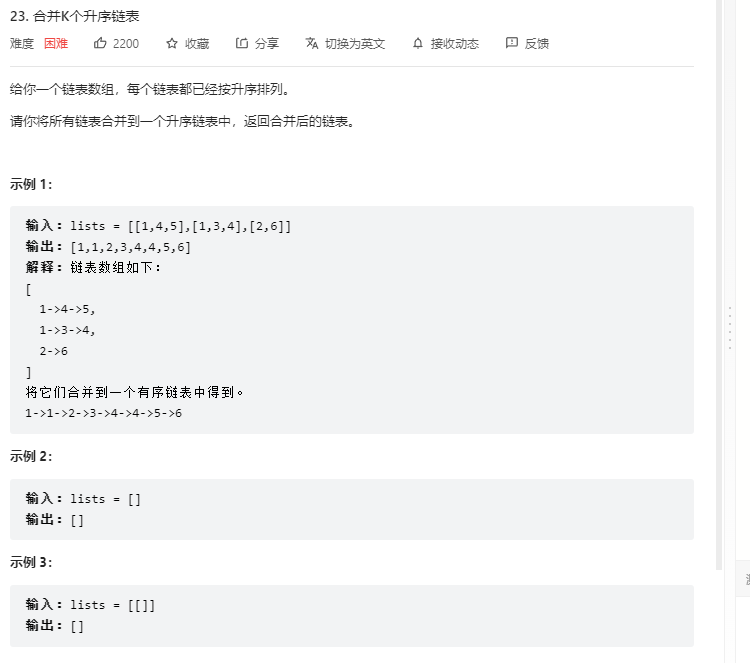
即归并分治
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 class Solution public ListNode mergeTwoLists (ListNode list1, ListNode list2) ListNode newList = new ListNode(); ListNode originList = newList; while (list1 != null && list2 != null ){ while (list1 != null && list2 != null && list1.val <= list2.val){ newList.next = list1; newList = newList.next; list1 = list1.next; } while (list1 != null && list2 != null && list2.val <= list1.val ){ newList.next = list2; newList = newList.next; list2 = list2.next; } } if (list1 == null ){ newList.next = list2; }else { newList.next = list1; } return originList.next; } public ListNode merge (ListNode[] lists, int left, int right) if (left == right) { return lists[left]; } if (left > right) { return null ; } int mid = (left + right) / 2 ; return mergeTwoLists(merge(lists, left, mid), merge(lists, mid + 1 , right)); } public ListNode mergeKLists (ListNode[] lists) return merge(lists, 0 , lists.length-1 ); } }
需要注意的是使用left == right来确定每一个都遍历到。
爆破遍历即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution : def strStr (self, haystack: str , needle: str ) -> int : i,j=0 ,0 res = len (haystack) for cIdx in range (len (haystack)): i = cIdx j = 0 if (haystack[i] == needle[j]): while (j < len (needle) and i < len (haystack) and haystack[i] == needle[j]): i += 1 j += 1 if (j == len (needle)): res = min (res,i - len (needle)) else : i += 1 if (res == len (haystack)): return -1 else : return res
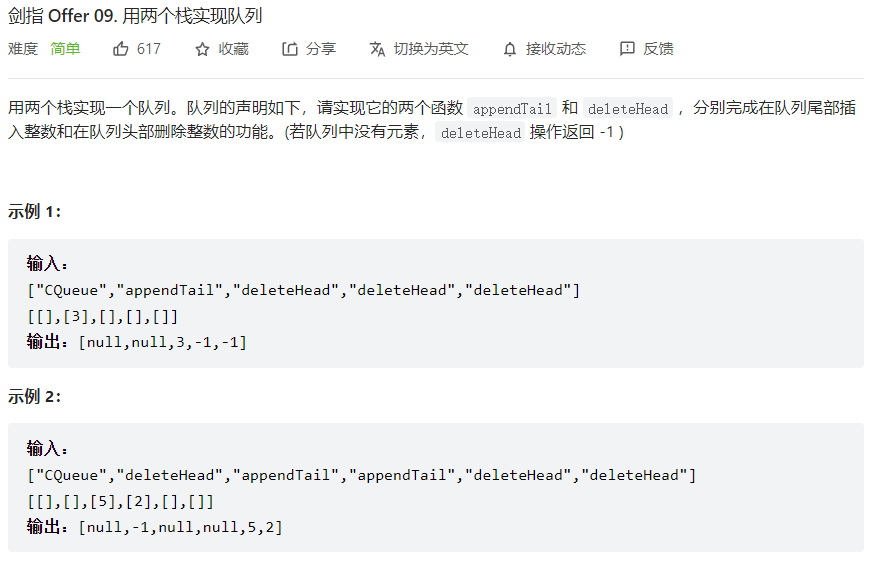
一个栈当输入,一个栈当输出
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class CQueue : def __init__ (self ): self.A = [] self.B = [] def appendTail (self, value: int ) -> None : self.A.append(value) def deleteHead (self ) -> int : if (len (self.B) != 0 ): return self.B.pop() else : while (len (self.A) != 0 ): self.B.append(self.A.pop()) if (len (self.B) == 0 ): return -1 else : return self.B.pop()
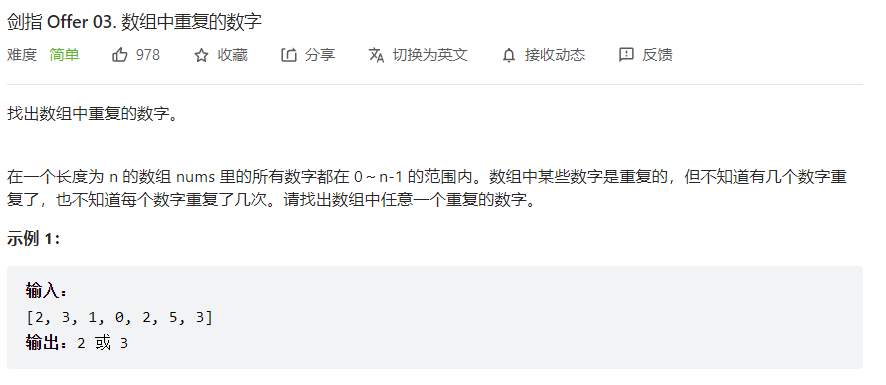
使用hash表即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 class Solution : def findRepeatNumber (self, nums: List [int ] ) -> int : hashset = set () for i in nums: if (i in hashset): return i else : hashset.add(i) return -1
先是自己写的,从尾部开始改变,时间耗费较多
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution : def reverseList (self, head: ListNode ) -> ListNode: if (head == None or head.next == None ): return head originHead = head n = 0 flag = 0 while (originHead.next != None ): head = originHead while (head.next != None ): tmp = head next = head.next head = next flag += 1 if (flag == 1 ): newHead = head tmp.next = None head.next = tmp return newHead
后面看题解,可以用多指针来代替,暂存前中后三个节点
剑指 Offer 24. 反转链表(迭代 / 递归,清晰图解) - 反转链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 class Solution : def reverseList (self, head: ListNode ) -> ListNode: pre = None cur = head while (cur != None ): tmp = cur.next cur.next = pre pre = cur cur = tmp return pre
同样的循环可以转化为递归
最优子数组的一般都能动态规划
动态规划
设dp[i]为以i为结尾的连续子数组和的最大值,即可得到状态转换方程
1 dp[i] = max(nums[i],dp[i-1] + nums[i])
依据状态转换方程得到代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class Solution : def maxSubArray (self, nums: List [int ] ) -> int : dp = [0 ] * len (nums) for i in range (len (nums)): if (i == 0 ): dp[i] = nums[0 ] res = dp[i] else : dp[i] = max (nums[i],dp[i-1 ] + nums[i]) res = max (res,dp[i]) return res
快慢指针
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class Solution : def getKthFromEnd (self, head: ListNode, k: int ) -> ListNode: originHead = head n = 0 while (n != k): n += 1 head = head.next while (head != None ): originHead = originHead.next head = head.next return originHead
动态规划,详见面试题46. 把数字翻译成字符串(动态规划,清晰图解) - 把数字翻译成字符串 - 力扣(LeetCode)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution : def translateNum (self, num: int ) -> int : numStr = str (num) dp = [0 ] * (len (numStr) + 1 ) for i in range (0 , len (numStr)): if (i == 0 ): dp[i] = 1 continue if (10 <= int (numStr[i - 1 ]) * 10 + int (numStr[i]) <= 25 ): if (i - 2 == -1 ): dp[i] = 2 continue dp[i] = dp[i - 2 ] + dp[i - 1 ] else : dp[i] = dp[i - 1 ] return dp[len (numStr) - 1 ]
需要注意的是组合的数字范围为1025,而不是025,因为01、02……不能进行组合翻译,我说怎么一直错
回溯加去重
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution : def permutation (self, s: str ) -> List [str ]: res = [] def back (s, tmp ): if (not s): res.append("" .join(tmp)) return for i in range (len (s)): tmpNums = s[:i] + s[i + 1 :] tmpTmp = tmp + [s[i]] back(tmpNums, tmpTmp) back(s, []) hashSet = set () for i in res: hashSet.add(i) return list (hashSet)
栈
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 class Solution : def reversePrint (self, head: ListNode ) -> List [int ]: stack = [] while (head != None ): stack.append(head.val) head = head.next res = [] while (len (stack) != 0 ): res.append(stack.pop()) return res
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution : F = [] def fib (self, n: int ) -> int : if (n == 0 ): return 0 if (n == 1 ): return 1 self.F = [0 ] * (n+1 ) self.F[0 ] = 0 self.F[1 ] = 1 i = 2 while ( i <= n): self.F[i] = (self.F[i-2 ] + self.F[i-1 ])% 1000000007 i += 1 return self.F[n]
但是还有时间复杂度更低的矩阵快速幂
参考官方解,时间复杂度为O(logn)
斐波那契数列 - 斐波那契数列 - 力扣(LeetCode)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 import numpy as npclass Solution : def fib (self, n: int ) -> int : def quickMi (num,power ): ans = 1 while (power > 0 ): if (power & 1 > 0 ): ans = np.dot(ans, num) % 1000000007 num = np.dot(num,num) power = power >> 1 return ans matrix = np.array([[1 , 1 ], [1 ,0 ]]) res = quickMi(matrix,n-1 ) return res[0 ][0 ]
顺子长度不一定为5时
先确定0的个数count,排除0,然后hash去重,得到hashSet
先判断去重后hashSet加count的长度是否还是为原数组长度,如果改变则代表有相同的非0元素,则不可能为顺子,直接False
判断此时listNums中最大和最小的差值是否小于等于0的个数count加len(listNums),小于等于则为True,否则为False
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 import randomfrom typing import List class Solution : def parition (self,nums,low,high ): pivot_idx = random.randint(low,high) pivot = nums[pivot_idx] left,right = low,high nums[left],nums[pivot_idx] = nums[pivot_idx],nums[left] while (left < right): while (left < right and nums[right] > pivot): right -= 1 nums[left] = nums[right] while (left < right and nums[left] <= pivot): left += 1 nums[right] = nums[left] nums[left] = pivot return left def quickSort (self,nums,low,high ): if (low > high): return mid = self.parition(nums,low,high) self.quickSort(nums,low,mid-1 ) self.quickSort(nums,mid+1 ,high) def sortArray (self,nums ): self.quickSort(nums,0 ,len (nums)-1 ) return nums def isStraight (self, nums: List [int ] ) -> bool : hashSet = set () count = 0 for i in nums: if (i == 0 ): count += 1 continue hashSet.add(i) if (len (hashSet) + count != len (nums)): return False listNums = list (hashSet) listNums = self.sortArray(listNums) if (listNums[len (listNums)-1 ] - listNums[0 ] <= count + len (listNums) - 1 ): return True else : return False
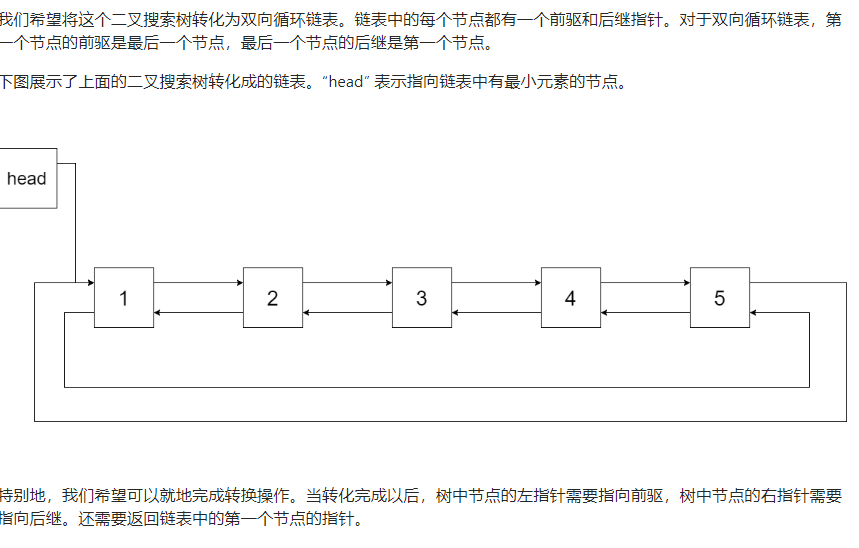
结合中序遍历的特点,加入处理
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 void inorderTraversal (Node cur) if (cur == null ) return ; inorderTraversal(cur.left); inorderTraversal(cur.right); }
然后每次处理的时候,利用前驱节点pre与当前节点cur进行处理
1 2 3 4 5 if (pre != null ){ pre.right = cur; cur.left = pre; pre = cur; }
当前驱节点pre为null时说明在遍历头节点,那么得到头节点,如下
1 2 3 4 else { head = cur; pre = cur; }
记得最后在头节点和尾部节点也要加入双向指针
1 2 head.left = pre; pre.right = head;
最终如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution Node pre, head; public Node treeToDoublyList (Node root) if (root == null ) return null ; inorderTraversal(root); head.left = pre; pre.right = head; return head; } void inorderTraversal (Node cur) if (cur == null ) return ; inorderTraversal(cur.left); if (pre != null ){ pre.right = cur; cur.left = pre; pre = cur; }else { head = cur; pre = cur; } inorderTraversal(cur.right); } }
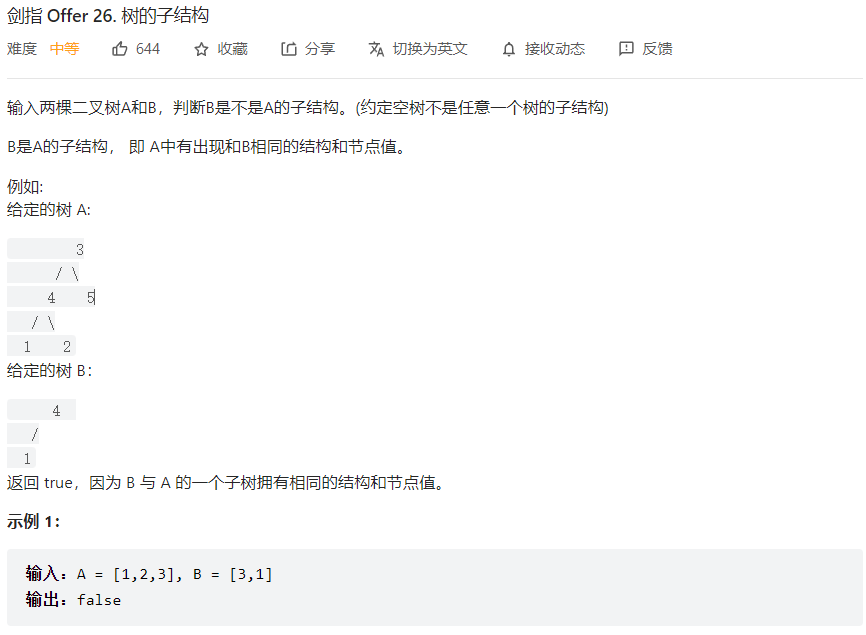
先找到结点数值相同的结点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 def findNode (self, rootA: TreeNode, rootB: TreeNode ): if (rootA == None or rootB == None ): return False if (rootA.val != rootB.val): return self.findNode(rootA.left, rootB) or self.findNode(rootA.right, rootB) else :
判断
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 def judge (self,rootA: TreeNode,rootB: TreeNode ): if (rootB == None ): return True if (rootA == None ): return False if (rootA.val == rootB.val and self.judge(rootA.left,rootB.left) and self.judge(rootA.right,rootB.right)): return True return False
最终结果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution : def judge (self,rootA: TreeNode,rootB: TreeNode ): if (rootB == None ): return True if (rootA == None ): return False if (rootA.val == rootB.val and self.judge(rootA.left,rootB.left) and self.judge(rootA.right,rootB.right)): return True return False def findNode (self, rootA: TreeNode, rootB: TreeNode ): if (rootA == None or rootB == None ): return False if (rootA.val != rootB.val): return self.findNode(rootA.left, rootB) or self.findNode(rootA.right, rootB) else : return self.judge(rootA.left,rootB.left) and self.judge(rootA.right,rootB.right) def isSubStructure (self, A: TreeNode, B: TreeNode ) -> bool : if (A == None or B == None ): return False if (A.val == B.val): if (self.judge(A,B) == False ): A.val = B.val + 1 else : return True return self.findNode(A, B)
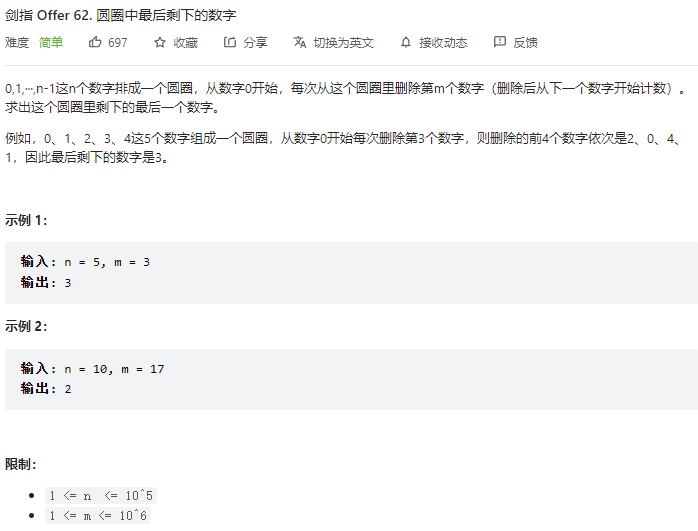
约瑟夫环问题,详情参考如下
换个角度举例解决约瑟夫环 - 圆圈中最后剩下的数字 - 力扣(LeetCode)
剑指 Offer 62. 圆圈中最后剩下的数字(数学 / 动态规划,清晰图解) - 圆圈中最后剩下的数字 - 力扣(LeetCode)
对于f(n,m)问题,固定m,对n做规律,得到状态转换方程
1 2 dp[n] = (dp[n-1] + m) % n dp[1] = 0
由此可得代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 class Solution : def lastRemaining (self, n: int , m: int ) -> int : dp = [0 ] * (n+1 ) for i in range (2 ,n+1 ): dp[i] = (dp[i-1 ] + m) % i return dp[n]
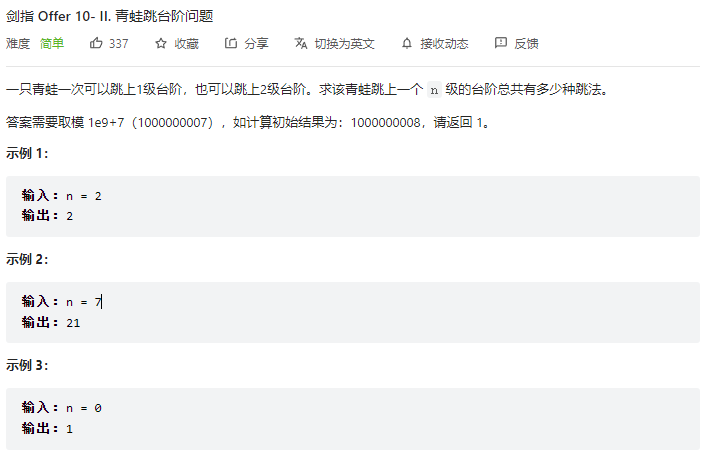
即类似之前的合并问题,把数字翻译成字符串
即推导一下,设每个台阶为1,每两个1台阶相邻可以选择合并为一个2台阶,那么假定如下台阶
此时如果加入一级台阶,有两种情况
与前一个台阶合并:1111 2
不合并:11111 1
即dp(6) = dp(4) + dp(5),由此可得动态规划
1 2 3 4 dp(0) = 1 dp(1) = 1 dp(2) = dp(0) + dp(1) = 2 dp(n) = dp(n-1) + dp(n-2)
依据动态规划得到解
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 class Solution : def numWays (self, n: int ) -> int : if (n == 0 or n == 1 ): return 1 dp = [0 ] * (n+1 ) dp[0 ] = 1 dp[1 ] = 1 for i in range (2 ,n+1 ): dp[i] = dp[i-1 ] + dp[i-2 ] return dp[n] % 1000000007
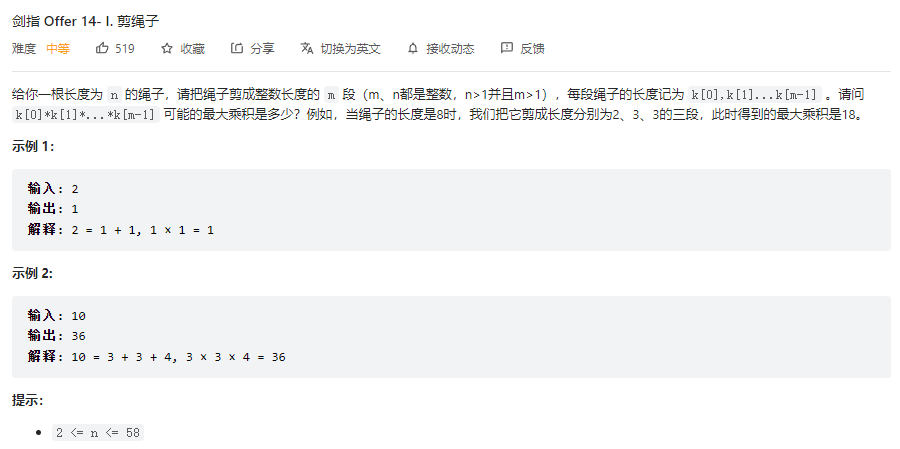
可用动态规划,dp[n]为将长度为n的绳子拆分为至少两截之后的乘积。假定将绳子拆分为j和剩下的n-j,那么如下
综上可得如下结果
1 dp[n] = j * max(n-j,dp[n-j])
然后定义初始状态
1 2 3 dp[0] = 0 dp[1] = 0 dp[2] = 1
可得最终代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class Solution : def cuttingRope (self, n: int ) -> int : dp = [0 ] * (n+1 ) dp[0 ] = 0 dp[1 ] = 0 dp[2 ] = 1 if (n == 0 or n == 1 or n == 2 ): return dp[n] for i in range (3 ,n+1 ): for j in range (1 ,i): dp[i] = max (dp[i],j*(i-j),j*dp[i-j]) return dp[n]
需要注意的是,遍历j的过程中,由于dp[i]会被重复计算,所以需要把dp[i]也加入进行判断,防止最大值被覆盖。
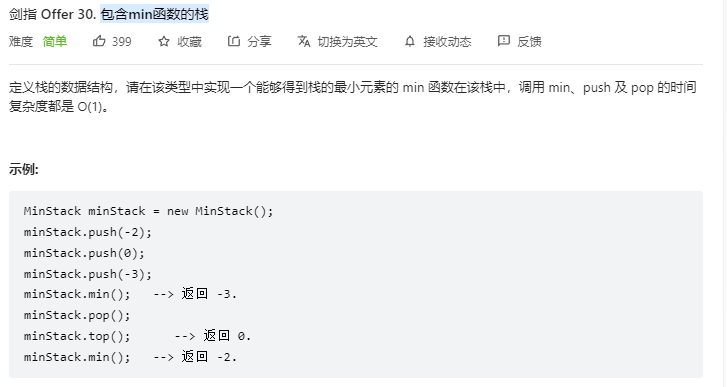
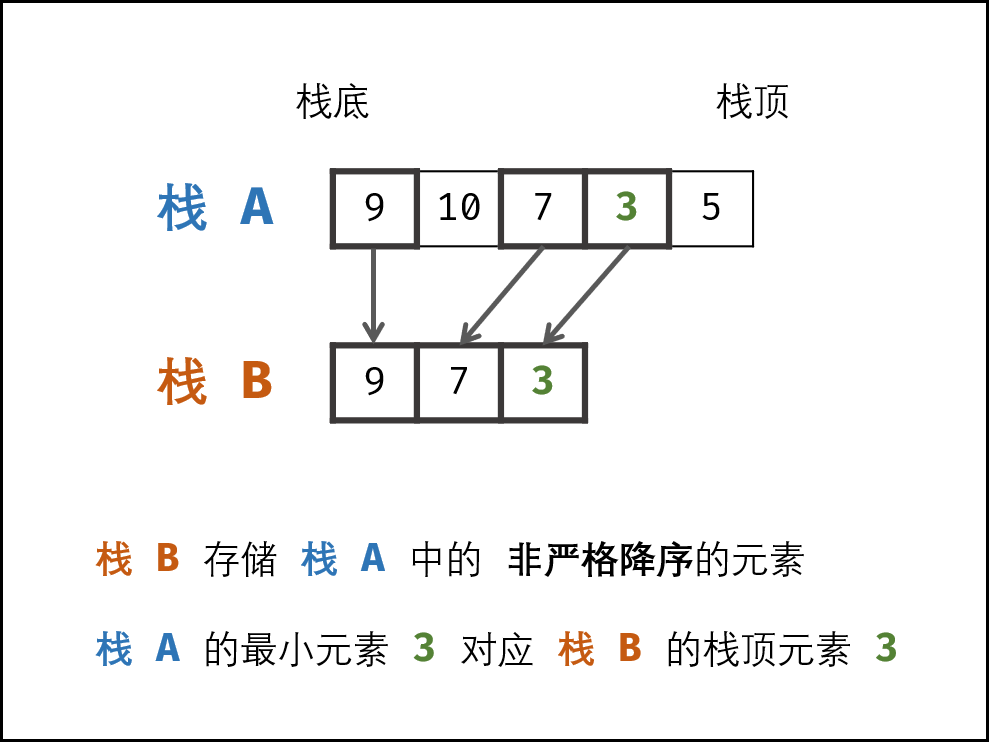
定义辅助栈,存放非严格递减元素,参考
面试题30. 包含 min 函数的栈(辅助栈,清晰图解) - 包含min函数的栈 - 力扣(LeetCode)
然后在pop和push函数中进行一下判断即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class MinStack : def __init__ (self ): self.stackA, self.stackB = [], [] def push (self, x: int ) -> None : self.stackA.append(x) if (len (self.stackB) == 0 or self.stackB[-1 ] >= x): self.stackB.append(x) def pop (self ) -> None : tmp = self.stackA.pop() if (tmp == self.stackB[-1 ]): self.stackB.pop() def top (self ) -> int : return self.stackA[-1 ] def min (self ) -> int : return self.stackB[-1 ]
双指针或直接新数组
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class Solution : def exchange (self, nums: List [int ] ) -> List [int ]: newJiNums = [] newOuNums = [] for i in nums: if (i % 2 == 1 ): newJiNums.append(i) else : newOuNums.append(i) return newJiNums + newOuNums
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class Solution : def exchange (self, nums: List [int ] ) -> List [int ]: i = 0 j = len (nums) - 1 while (i < j): while (i < j and nums[i] % 2 == 1 ): i += 1 while (i < j and nums[j] % 2 == 0 ): j -= 1 nums[i],nums[j] = nums[j],nums[i] return nums
刚开始想着行不行保存状态,a,b,c保存状态,初始化为0,然后每次将这三个数尝试递增之后,计算tmp = min((a+1)*2,(b+1)*3,(c+1)*5),然后取最小值,之后再判断是哪一个,将对应的a/b/c加一即可。
然后由于a+1/b+1/c+1可能会出现包含除2,3,5之外的质因子,所以需要进行判断,判断其最大的质因子是否大于5即可,如果大于5,则不能要这个数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 class Solution : def get_num_factors (self,num ): hashSet = set () tmp = 2 if (num < tmp): return [] while (num >= tmp): k = num % tmp if (k == 0 ): hashSet.add(tmp) num = num / tmp else : tmp = tmp + 1 hashList = list (hashSet) return hashList def nthUglyNumber (self, n: int ) -> int : a,b,c = 0 ,0 ,0 tmp = [2 ,3 ,5 ] dp = [1 ] * (n+1 ) i = 2 while (i < n+1 ): flag = 0 tmp = min ((a+1 )*2 ,(b+1 )*3 ,(c+1 )*5 ) if (tmp == (a+1 )*2 ): tmpList = self.get_num_factors(a+1 ) tmpList.sort() if (len (tmpList) > 0 and tmpList[-1 ] > 5 ): a += 1 else : if (not flag): i += 1 flag = 1 a += 1 if (tmp == (b+1 )*3 ): tmpList = self.get_num_factors(b+1 ) tmpList.sort() if (len (tmpList) > 0 and tmpList[-1 ] > 5 ): b += 1 else : if (not flag): i += 1 flag = 1 b += 1 if (tmp == (c+1 )*5 ): tmpList = self.get_num_factors(c+1 ) tmpList.sort() if (len (tmpList) > 0 and tmpList[-1 ] > 5 ): c += 1 else : if (not flag): i += 1 flag = 1 c += 1 if (flag): dp[i-1 ] = tmp return dp[n]
时间复杂度为O(n^2),会超时,后面看题解用动态规划才行,参考
剑指 Offer 49. 丑数(动态规划,清晰图解) - 丑数 - 力扣(LeetCode)
需要明确一点就是,所有的丑数都是前面的某个丑数乘以某个数得到的,这个某个数也必定是某个丑数,不然就会存在非1,2,3,5的质因子了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution : def nthUglyNumber (self, n: int ) -> int : state = [0 ,0 ,0 ] dp = [1 ] * (n + 1 ) for i in range (2 ,n+1 ): dp[i] = min (dp[state[0 ]+1 ]*2 ,dp[state[1 ]+1 ]*3 ,dp[state[2 ]+1 ]*5 ) if (dp[i] == dp[state[0 ]+1 ]*2 ): state[0 ] += 1 if (dp[i] == dp[state[1 ]+1 ]*3 ): state[1 ] += 1 if (dp[i] == dp[state[2 ]+1 ]*5 ): state[2 ] += 1 return dp[n]
和之前的买卖股票最佳时机 一样
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 class Solution: def maxProfit(self, prices: List[int]) -> int: minIdx = 0 maxBenefit = 0 for i in range(0,len(prices)): if(prices[i] < prices[minIdx]): minIdx = i maxBenefit = max(maxBenefit,prices[i] - prices[minIdx]) return maxBenefit
不过这次分析一下动态规划,参考面试题63. 股票的最大利润(动态规划,清晰图解) - 股票的最大利润 - 力扣(LeetCode)
假定dp[i]代表以prices[i]为结尾的子数组的最大利润,则可推导得到动态转换方程
1 2 前i日最大利润=max(前(i−1)日最大利润,第i日价格−前i日最低价格) dp[i] = max(dp[i-1],prices[i]-min(prices[0:i]))
依据动态转换方程求得最终代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class Solution : def maxProfit (self, prices: List [int ] ) -> int : if (len (prices) == 0 ): return 0 minIdx = 0 dp = [0 ] * len (prices) dp[0 ] = 0 for i in range (1 ,len (prices)): if (prices[i] < prices[minIdx]): minIdx = i dp[i] = max (dp[i-1 ],prices[i] - prices[minIdx]) return dp[len (prices)-1 ]
参考之前的无重复字符的最长子串 ,使用滑动窗口+哈希
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution : def lengthOfLongestSubstring (self, s: str ) -> int : if (len (s) == 0 ): return 1 i,j=0 ,0 tmpS = "" maxLen = 0 while (j < len (s)): if (s[j] in tmpS): i += 1 j += 1 tmpS = s[i:j] while (len (set (tmpS)) != len (tmpS)): i += 1 tmpS = s[i:j] maxLen = max (maxLen,j-i)
或者使用动态规划+哈希
假定dp[i]为以s[0:i]这个子字符串的无重复字符的最长字串长度,当加入一个字符,即对于dp[i+1]而言,如果加入的字符s[i+1]可以和前面s[i-dp[i-1]:i]组成无重复的子字符串,那么dp[i+1] = dp[i] + 1,否则dp[i+1] = dp[i]
1 2 3 判断加入字符是否可以和前面dp[i-1]个字符串组成无重复子串,推导得到下面的状态转换方程 dp[i] = dp[i-1] = dp[i-1] + 1
初始状态:dp[0] = 1
依据状态转换方程可得代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution : def lengthOfLongestSubstring (self, s: str ) -> int : if (len (s) == 0 ): return 0 if (len (s) == 1 ): return 1 dp = [0 ] * (len (s)) dp[0 ] = 1 for i in range (1 ,len (s)): tmpS = s[i-dp[i-1 ]:i+1 ] if (len (set (tmpS)) == len (tmpS)): dp[i] = dp[i-1 ] + 1 else : dp[i] = dp[i-1 ] return dp[len (s)-1 ]
利用两次遍历依次累乘
对于B[i]:
第一次遍历,计算从B[0]~B[i-1]的乘积,结果保存在B[i]中
这时候由于B[i] = B[i-1]*A[i-1],所以我们可以从B[0]依次累乘,只需要遍历一次即可。
第二次遍历,计算从B[n-1]~B[i+1]的乘积,最后乘上之前保存的B[i]即可
同样这时候由于B[i] = B[i+1]*A[i+1]*B[i],那么我们也可以从B[n-1]开始依次累乘,遍历一次即可。
依据该规律,两次遍历即可得出结果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution : def constructArr (self, a: List [int ] ) -> List [int ]: product = 1 b = [1 ] * len (a) for i in range (0 ,len (a)): if (i == 0 ): product = 1 else : product *= a[i-1 ] b[i] = product product = 1 for i in range (len (a)-1 ,-1 ,-1 ): if (i == len (a) - 1 ): product = 1 else : product *= a[i+1 ] b[i] *= product return b
如果不考虑空间复杂度,直接使用hash即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution: def singleNumbers(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[int]: dict = {} myList = [] for i in nums: if(i in dict.keys()): dict[i] = not dict[i] else: dict[i] = True for i in dict.keys(): if(dict[i] == True): myList.append(i) return myList
但是要求空间复杂度为O(1),那么就需要进行其他方法了,参考
剑指 Offer 56 - I. 数组中数字出现的次数(位运算,清晰图解) - 数组中数字出现的次数 - 力扣(LeetCode)
提供的思路,位运算
假设不同的两位数分别为x,y
通过异或nums里所有数,求得x⊕y为xy
假定m=1,通过位运算逐次循环左移并且异或x⊕y,求得x⊕y中最小为1的位。
由于x⊕y中某位bit为1,那么由于异或的特性,x、y各自该位的bit一定一个为1一个为0,基于此对nums进行分组
将该位bit为1的分为一组,为0的分为另一组,那么即可将x、y分开。同时对于其他的数字,由于各自独立成对,那么成对的数字一定会被分到同一组,之后异或之后也直接为0了。
然后各自两种进行异或即可得到最终的x、y
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution : def singleNumbers (self, nums: List [int ] ) -> List [int ]: xy = 0 for i in nums: xy ^= i m = 1 while (m & xy == 0 ): m <<= 1 x,y = 0 ,0 for i in nums: if (i & m == 0 ): x ^= i else : y ^= i return [x,y]
动态规划,设dp[i][j]为以[i,j]为终点的途径的获得的最大价值礼物,则有状态转换方程如下
1 dp[i][j] = max(dp[i-1][j],dp[i][j-1]) + grid[i][j]
初始状态:dp[0][0] = grid[0][0]
同时由于可能会超出边界,所以将dp扩大一个长宽
1 dp = [[0 for i in range(len(grid[0]) + 1)] for i in range(len(grid) + 1)]
同时从dp[1][1]开始作为计数,边界为数值为0,依据状态转换方程可得
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 class Solution : def maxValue (self, grid: List [List [int ]] ) -> int : dp = [[0 for i in range (len (grid[0 ]) + 1 )] for i in range (len (grid) + 1 )] dp[1 ][1 ] = grid[0 ][0 ] for i in range (1 , len (grid) + 1 ): for j in range (1 , len (grid[0 ]) + 1 ): dp[i][j] = max (dp[i-1 ][j],dp[i][j-1 ]) + grid[i - 1 ][j - 1 ] return dp[len (grid)][len (grid[0 ])]
第一个想法就是hash表
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution : def majorityElement (self, nums: List [int ] ) -> int : if (len (nums) == 1 ): return nums[0 ] dict = {} for i in nums: if (i in dict .keys()): dict [i] = dict [i] + 1 else : dict [i] = 1 for i in dict : if (dict [i] > len (nums)//2 ): return i
第二个想法就是排序,然后取中位数即为超过数组一半的数
第三个参考摩尔投票法:
剑指 Offer 39. 数组中出现次数超过一半的数字(摩尔投票法,清晰图解) - 数组中出现次数超过一半的数字 - 力扣(LeetCode)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class Solution : def majorityElement (self, nums: List [int ] ) -> int : sum = 0 for i in nums: if (sum == 0 ): x = i if (i != x): sum -= 1 else : sum += 1 return x
和求最长不重复子串一样,直接滑动窗口
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution : def findContinuousSequence (self, target: int ) -> List [List [int ]]: i,j = 0 ,0 myList = [i for i in range (1 ,ceil(target/2 )+1 )] res = [] sum = 0 sum += myList[i] while (j < len (myList)): if (sum < target): if (j == len (myList)-1 ): return res else : j += 1 sum += myList[j] elif (sum == target): res.append(myList[i:j+1 ]) if (j == len (myList)-1 ): return res else : j += 1 sum += myList[j] else : sum -= myList[i] i += 1 return res
可知BFS广度优先搜索满足要求,使用队列
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 import queueclass Solution : def levelOrder (self, root: TreeNode ) -> List [int ]: res = [] q = queue.Queue() def bfs (): if (q.qsize() == 0 ): return root = q.get() if (root == None ): return res.append(root.val) if (root.left != None ): q.put(root.left) if (root.right != None ): q.put(root.right) bfs() q.put(root) bfs() return res
去掉这个递归有点麻烦,多次判断,尝试去掉递归
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 import queueclass Solution : def levelOrder (self, root: TreeNode ) -> List [int ]: res = [] q = queue.Queue() def bfs (): while (q.qsize() != 0 ): tmpRoot = q.get() res.append(tmpRoot.val) if (tmpRoot.left != None ): q.put(tmpRoot.left) if (tmpRoot.right != None ): q.put(tmpRoot.right) if (root == None ): return res q.put(root) bfs() return res
使用pre、cur、next三指针进行,需要注意某些特殊条件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 struct ListNode* reverseBetween (struct ListNode* head, int m, int n ) { struct ListNode * originHead = struct ListNode * pre = struct ListNode * cur = struct ListNode * tmpHead = struct ListNode * lengtHead = if ((n-m) < 1 || head==NULL ||head->next==NULL ) { return originHead; } if (m == 1 ) { tmpHead = NULL ; } for (int i = 0 ; i < m - 1 ; i ++ ) { cur = cur->next; } for (int i = 0 ; i < n ; i ++ ) { pre = pre->next; } struct ListNode * next ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n - m + 1 ; i ++) { next = cur->next; cur->next = pre; pre = cur; cur = next; } if (tmpHead == NULL ) { return pre; } else { for (int i = 0 ; i < m - 2 ; i ++ ) { tmpHead = tmpHead->next; } tmpHead->next = pre; return originHead; } }
即依照索引,滑动窗口形式进行指定区间翻转,这里要记录一下翻转之前的preHead指针,方便在翻转之后进行连接。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 struct ListNode* reverseKGroup(struct ListNode* head, int k ) { if (k = = 1 ) { return head; } struct ListNode* originHead = head; struct ListNode* lengtHead = head; struct ListNode* pre = head; struct ListNode* cur = head; struct ListNode* preHead; struct ListNode* nextPreHead = NULL ; int tmpCount; int left = 1 ; int right = left + k - 1 ; int length = 0 ; while (lengtHead != NULL ) { lengtHead = lengtHead- > next; length + = 1 ; } while (right <= length) { tmpCount = 0 ; while (tmpCount < k) { pre = pre- > next; tmpCount + = 1 ; } struct ListNode* next; for (int j = 0 ; j < k; j + + ) { if (j = = 0 ) { preHead = nextPreHead; nextPreHead = cur; } next = cur- > next; cur- > next = pre; pre = cur; cur = next; } if (left = = 1 ) { originHead = pre; } if (preHead != NULL ) { preHead- > next = pre; } pre = cur; left + = k; right + = k; } return originHead; }
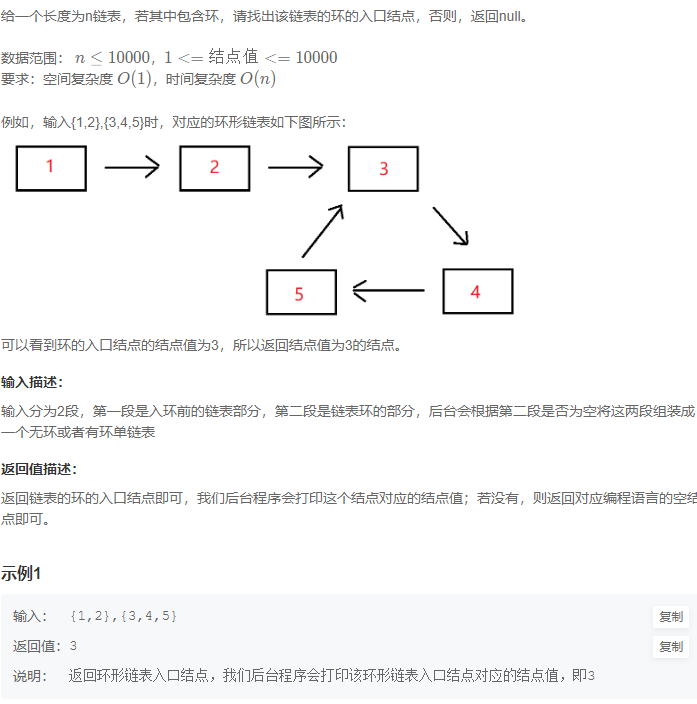
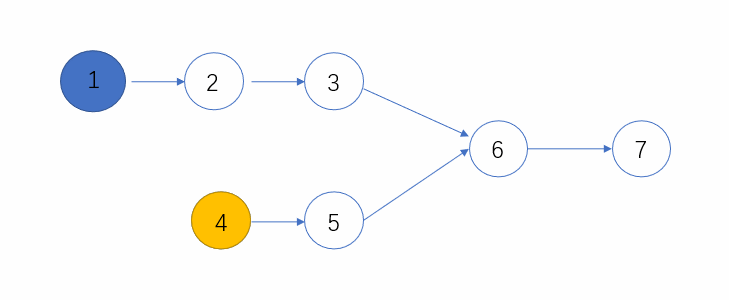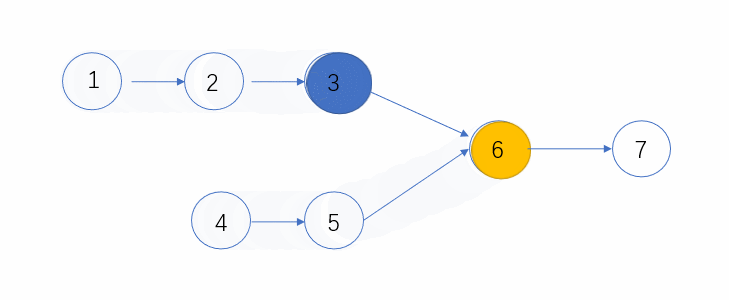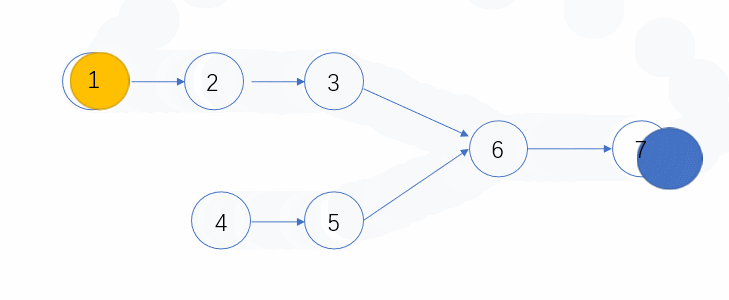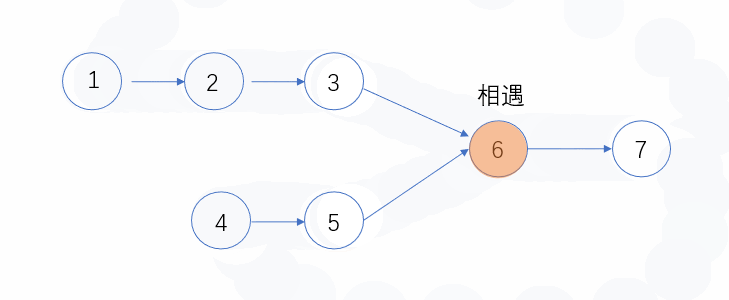
快慢指针,参考:链表中环的入口结点_牛客题霸_牛客网 (nowcoder.com)
快指针走两步,慢指针走一步,直至相遇
从相遇点和链表头部再出发,直至相遇,相遇点即为环入口点。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution {public : ListNode* EntryNodeOfLoop (ListNode* head) { struct ListNode * fast = struct ListNode * low = struct ListNode * originHead = while (fast&&fast->next){ fast = fast->next->next; low = low->next; if (fast==low) break ; } if (fast == NULL or fast->next == NULL ){ return NULL ; } while (originHead != fast){ originHead = originHead->next; fast = fast->next; } return originHead; } };
快慢指针,记得记录pre节点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 class Solution {public : ListNode* removeNthFromEnd (ListNode* pHead, int k) { struct ListNode * fast = struct ListNode * pre =NULL ; struct ListNode * slow = int tmp = 0 ; while (fast != NULL && tmp != k){ fast = fast->next; tmp += 1 ; } if (tmp != k){ return NULL ; } while (fast != NULL ){ fast = fast->next; if (pre == NULL ){ pre = slow; } else { pre = pre->next; } slow = slow->next; } if (pre == NULL ){ return pHead->next; } else { pre->next = slow->next; } return pHead; } };
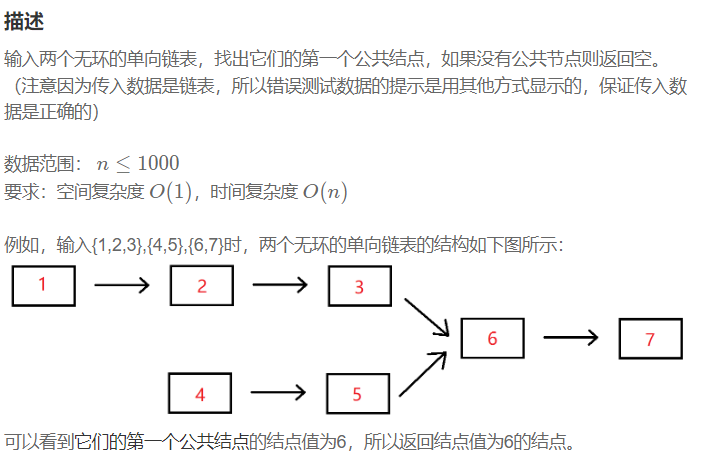
计算长度,参考:两个链表的第一个公共结点_牛客题霸_牛客网 (nowcoder.com)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution {public : ListNode* FindFirstCommonNode ( ListNode* pHead1, ListNode* pHead2) { struct ListNode * originHead1 = struct ListNode * originHead2 = while (pHead1 != pHead2){ if (pHead1 == NULL ){ pHead1 = originHead2; }else { pHead1 = pHead1->next; } if (pHead2 == NULL ){ pHead2 = originHead1; }else { pHead2 = pHead2->next; } } return pHead1; } };
分别简历奇偶链表然后串在一起,注意边界问题
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution {public : ListNode* oddEvenList (ListNode* head) { if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL ){ return head; } ListNode* oddHead = head; ListNode* evenHead = head->next; ListNode* originOddHead = head; ListNode* originEvenHead = evenHead; while (oddHead->next != NULL && evenHead->next != NULL ){ oddHead->next = oddHead->next->next; oddHead = oddHead->next; evenHead->next = evenHead->next->next; evenHead = evenHead->next; } oddHead->next = originEvenHead; return originOddHead; } };
需要最后cur为NULL时,如果最后一个也需要删除,那么此时由于cur为NULL,所以无法进入while循环中,无法删除,需要在while循环外部进行判断
1 2 3 if (pre->val == tmp){ preHead->next = NULL ; }
最终结果
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 class Solution {public : ListNode* deleteDuplicates (ListNode* head) { if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL ){ return head; } struct ListNode * preHead =malloc (0x10 ); struct ListNode * originPreHead = preHead->next = head; struct ListNode * pre = struct ListNode * cur = int tmp; while (cur != NULL ){ if ( cur->val == pre->val){ tmp = cur->val; preHead->next = pre->next; pre = pre->next; cur = cur->next; }else { if (pre->val == tmp){ preHead->next = cur; } else { preHead = preHead->next; } cur = cur->next; pre = pre->next; } } if (pre->val == tmp){ preHead->next = NULL ; } return originPreHead->next; } };
注意边界性问题
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 int search (int * nums, int numsLen, int target ) int l = 0 ; int r = numsLen - 1 ; int mid = (l + r)/2 ; while (r >= l){ if (nums[mid] == target){ return mid; } if (nums[mid] < target){ l = mid + 1 ; mid = (mid+1 + r) / 2 ; } else { r = mid - 1 ; mid = (l + mid-1 ) / 2 ; } } return -1 ; }
采用二分查找,依据mid来更改right和left缩小范围,直至找到峰值
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution {public : int findPeakElement (vector<int >& nums) int l = 0 ; int r = nums.size () - 1 ; while (l < r){ int mid = (l + r)/2 ; if (nums[mid] > nums[mid+1 ]){ r = mid; } else { l = mid + 1 ; } } return l; } };
例题均来源于Leetcode
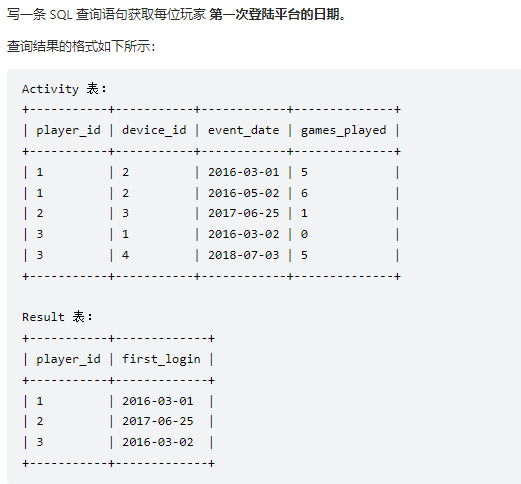
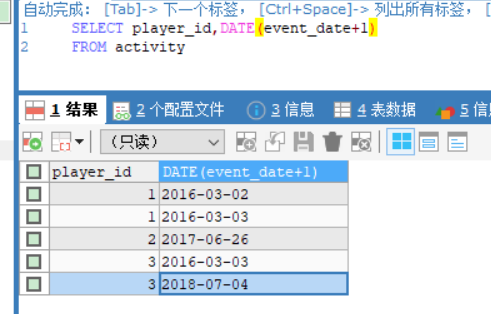
创建语句
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Create table If Not Exists Activity (player_id int , device_id int , event_date date , games_played int );Truncate table Activity;insert into Activity (player_id, device_id, event_date, games_played) values ('1' , '2' , '2016-03-01' , '5' );insert into Activity (player_id, device_id, event_date, games_played) values ('1' , '2' , '2016-05-02' , '6' );insert into Activity (player_id, device_id, event_date, games_played) values ('2' , '3' , '2017-06-25' , '1' );insert into Activity (player_id, device_id, event_date, games_played) values ('3' , '1' , '2016-03-02' , '0' );insert into Activity (player_id, device_id, event_date, games_played) values ('3' , '4' , '2018-07-03' , '5' );
基于group by之后的列字段进行相同值的聚合,当查询多个列时,通常需要进行排序,所以也需要对相关数据进行值判定
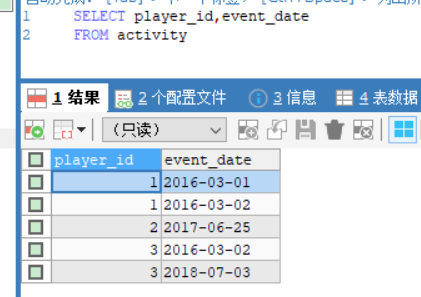
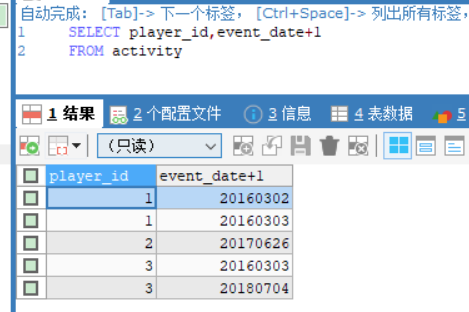
1 2 3 4 5 SELECT player_id, min (event_date) first_login FROM ActivityGROUP BY player_id
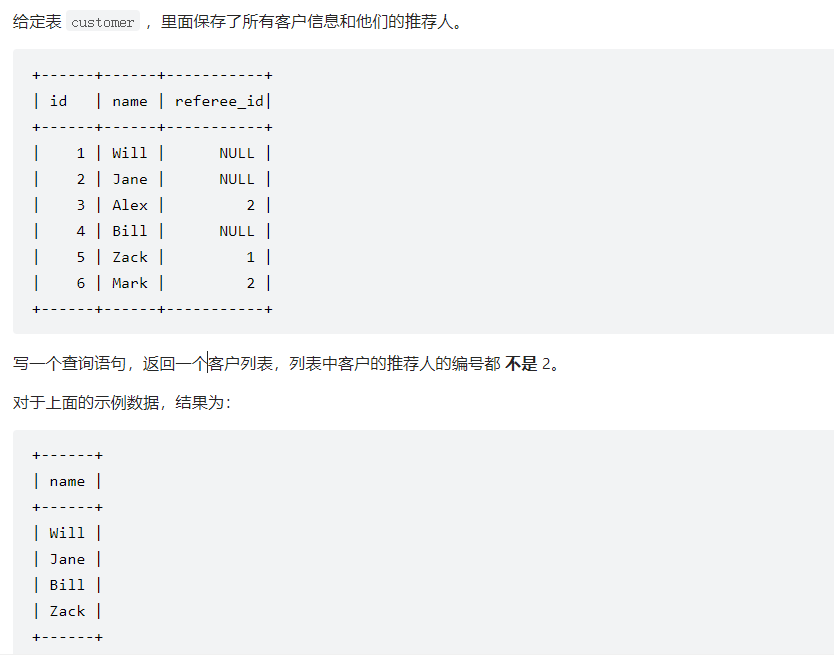
创建语句:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Create table If Not Exists Customer (id int , name varchar (25 ), referee_id int );Truncate table Customer;insert into Customer (id, name, referee_id) values ('1' , 'Will' , 'None' );insert into Customer (id, name, referee_id) values ('2' , 'Jane' , 'None' );insert into Customer (id, name, referee_id) values ('3' , 'Alex' , '2' );insert into Customer (id, name, referee_id) values ('4' , 'Bill' , 'None' );insert into Customer (id, name, referee_id) values ('5' , 'Zack' , '1' );insert into Customer (id, name, referee_id) values ('6' , 'Mark' , '2' );
参考:寻找用户推荐人 - 寻找用户推荐人 - 力扣(LeetCode)
MySQL 使用三值逻辑 —— TRUE, FALSE 和 UNKNOWN。任何与 NULL 值进行的比较都会与第三种值UNKNOWN做比较。这个“任何值”包括 NULL 本身!这就是为什么 MySQL 提供 IS NULL 和 IS NOT NULL 两种操作来对 NULL 特殊判断。
1 SELECT name FROM customer WHERE referee_id != 2 OR referee_id IS NULL;
创建语句:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Create table If Not Exists Users (user_id int , join_date date , favorite_brand varchar (10 ));Create table If Not Exists Orders (order_id int , order_date date , item_id int , buyer_id int , seller_id int );Create table If Not Exists Items (item_id int , item_brand varchar (10 ))Truncate table Users;insert into Users (user_id, join_date, favorite_brand) values ('1' , '2018-01-01' , 'Lenovo' );insert into Users (user_id, join_date, favorite_brand) values ('2' , '2018-02-09' , 'Samsung' );insert into Users (user_id, join_date, favorite_brand) values ('3' , '2018-01-19' , 'LG' );insert into Users (user_id, join_date, favorite_brand) values ('4' , '2018-05-21' , 'HP' );Truncate table Orders;insert into Orders (order_id, order_date, item_id, buyer_id, seller_id) values ('1' , '2019-08-01' , '4' , '1' , '2' );insert into Orders (order_id, order_date, item_id, buyer_id, seller_id) values ('2' , '2018-08-02' , '2' , '1' , '3' );insert into Orders (order_id, order_date, item_id, buyer_id, seller_id) values ('3' , '2019-08-03' , '3' , '2' , '3' );insert into Orders (order_id, order_date, item_id, buyer_id, seller_id) values ('4' , '2018-08-04' , '1' , '4' , '2' );insert into Orders (order_id, order_date, item_id, buyer_id, seller_id) values ('5' , '2018-08-04' , '1' , '3' , '4' );insert into Orders (order_id, order_date, item_id, buyer_id, seller_id) values ('6' , '2019-08-05' , '2' , '2' , '4' );Truncate table Items;insert into Items (item_id, item_brand) values ('1' , 'Samsung' );insert into Items (item_id, item_brand) values ('2' , 'Lenovo' );insert into Items (item_id, item_brand) values ('3' , 'LG' );insert into Items (item_id, item_brand) values ('4' , 'HP' );
以左表为基础,从右表中选择对应条件的数据添加。
这里即以table1为基础,从table2中选择对应条件数据
如果 x1 为 NULL, 返回 x2,否则返回 x1。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 SELECT users.user_id AS buyer_id, users.join_date, IFNULL(userBy.cnt,0) AS orders_in_2019 FROM users LEFT JOIN( SELECT buyer_id, COUNT(buyer_id) AS cnt FROM orders WHERE orders.`order_date` BETWEEN '2019-01-01' AND '2019-12-31' GROUP BY buyer_id )userBy ON users.user_id = userBy.buyer_id
创建语句:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Create table If Not Exists Activity (user_id int , session_id int , activity_date date , activity_type ENUM('open_session' , 'end_session' , 'scroll_down' , 'send_message' ));Truncate table Activity;insert into Activity (user_id, session_id, activity_date, activity_type) values ('1' , '1' , '2019-07-20' , 'open_session' );insert into Activity (user_id, session_id, activity_date, activity_type) values ('1' , '1' , '2019-07-20' , 'scroll_down' );insert into Activity (user_id, session_id, activity_date, activity_type) values ('1' , '1' , '2019-07-20' , 'end_session' );insert into Activity (user_id, session_id, activity_date, activity_type) values ('2' , '4' , '2019-07-20' , 'open_session' );insert into Activity (user_id, session_id, activity_date, activity_type) values ('2' , '4' , '2019-07-21' , 'send_message' );insert into Activity (user_id, session_id, activity_date, activity_type) values ('2' , '4' , '2019-07-21' , 'end_session' );insert into Activity (user_id, session_id, activity_date, activity_type) values ('3' , '2' , '2019-07-21' , 'open_session' );insert into Activity (user_id, session_id, activity_date, activity_type) values ('3' , '2' , '2019-07-21' , 'send_message' );insert into Activity (user_id, session_id, activity_date, activity_type) values ('3' , '2' , '2019-07-21' , 'end_session' );insert into Activity (user_id, session_id, activity_date, activity_type) values ('4' , '3' , '2019-06-25' , 'open_session' );insert into Activity (user_id, session_id, activity_date, activity_type) values ('4' , '3' , '2019-06-25' , 'end_session' );
去重,直接当作函数用即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 SELECT Activity.`activity_date` AS `day `, COUNT (DISTINCT (Activity.`user_id`)) AS active_users FROM ActivityWHERE Activity.`activity_date` BETWEEN '2019-06-28' AND '2019-07-27' GROUP BY Activity.`activity_date`
创建语句:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS Tree (id INT, p_id INT); TRUNCATE TABLE Tree; INSERT INTO Tree (id, p_id) VALUES ('1', 'None'); INSERT INTO Tree (id, p_id) VALUES ('2', '1'); INSERT INTO Tree (id, p_id) VALUES ('3', '1'); INSERT INTO Tree (id, p_id) VALUES ('4', '2'); INSERT INTO Tree (id, p_id) VALUES ('5', '2');
union联合查询:
将多个查询语句联合起来
这里首先分类为根节点、叶子节点、内部节点
然后将三个表联合起来,排个序即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 SELECT id, 'Root' AS TYPE FROM treeWHERE p_id IS NULL UNION SELECT id,'Inner' AS TYPEFROM treeWHERE id IN (SELECT p_id FROM tree WHERE p_id IS NOT NULL ) AND p_id IS NOT NULL UNION SELECT id,'Leaf' AS TYPEFROM treeWHERE id NOT IN (SELECT p_id FROM tree WHERE p_id IS NOT NULL ) AND p_id IS NOT NULL ORDER BY id;
CASE语句查询:
形式为case-when-then-else-end
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 SELECT id, CASE WHEN p_id IS NULL THEN 'Root' #root WHEN id IN (SELECT p_id FROM tree WHERE p_id IS NOT NULL ) THEN 'Inner' #inner ELSE 'Leaf' #leaf END AS TYPE FROM treeORDER BY id;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Create table If Not Exists ActorDirector (actor_id int , director_id int , timestamp int );Truncate table ActorDirector;insert into ActorDirector (actor_id, director_id, timestamp ) values ('1' , '1' , '0' );insert into ActorDirector (actor_id, director_id, timestamp ) values ('1' , '1' , '1' );insert into ActorDirector (actor_id, director_id, timestamp ) values ('1' , '1' , '2' );insert into ActorDirector (actor_id, director_id, timestamp ) values ('1' , '2' , '3' );insert into ActorDirector (actor_id, director_id, timestamp ) values ('1' , '2' , '4' );insert into ActorDirector (actor_id, director_id, timestamp ) values ('2' , '1' , '5' );insert into ActorDirector (actor_id, director_id, timestamp ) values ('2' , '1' , '6' );
主要是having的知识点
参考:mysql having和where的区别 - caibaotimes - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
where:
是作用在查询结果进行分组之前,过滤掉不符合条件的数据。
where中不能包含聚合函数。(注意是:where后面子句不能有聚合函数,而在含有where中可以使用聚合函数)
作用在group by和having字句前
是作用于对表与视图
having:
是作用在查询结果分组之后,筛选满足条件的组,过滤掉数据。
通常跟聚合函数一起使用。
having子句在聚合后对组记录进行筛选。
是作用于分组
其实就是group by的时候用到having来进行分组后的条件筛选,而不能用where,where是分组之前使用
1 2 3 4 SELECT actor_id,director_idFROM ActorDirectorGROUP BY ActorDirector.actor_id,ActorDirector.director_idHAVING COUNT (ActorDirector.director_id)>= 3
或者先计数然制表,然后再查询也行
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 SELECT actor_id,director_id FROM ( SELECT actor_id,director_id,COUNT (director_id) AS cnt FROM ActorDirector GROUP BY ActorDirector.actor_id,ActorDirector.director_id ) cntTable WHERE cntTable.cnt >= 3
创建语句
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Create table If Not Exists Activity (player_id int , device_id int , event_date date , games_played int );Truncate table Activity;insert into Activity (player_id, device_id, event_date, games_played) values ('1' , '2' , '2016-03-01' , '5' );insert into Activity (player_id, device_id, event_date, games_played) values ('1' , '2' , '2016-03-02' , '6' );insert into Activity (player_id, device_id, event_date, games_played) values ('2' , '3' , '2017-06-25' , '1' );insert into Activity (player_id, device_id, event_date, games_played) values ('3' , '1' , '2016-03-02' , '0' );insert into Activity (player_id, device_id, event_date, games_played) values ('3' , '4' , '2018-07-03' , '5' );
Date数据类型及函数:
mysql支持date日期数据类型以及为其创建了一个DATE函数,用法如下
可以使用CONVERT或者TRUNCATE来对除法进行保留小数
CONVERT(a/b,DECIMAL(10,2))
代表a/b以10精度计算,保留2位小数,这个精度也算是小数点后几位,存在四舍五入
TRUNCATE(a/b,2)
代表a/b保留2位小数,但是没有四舍五入
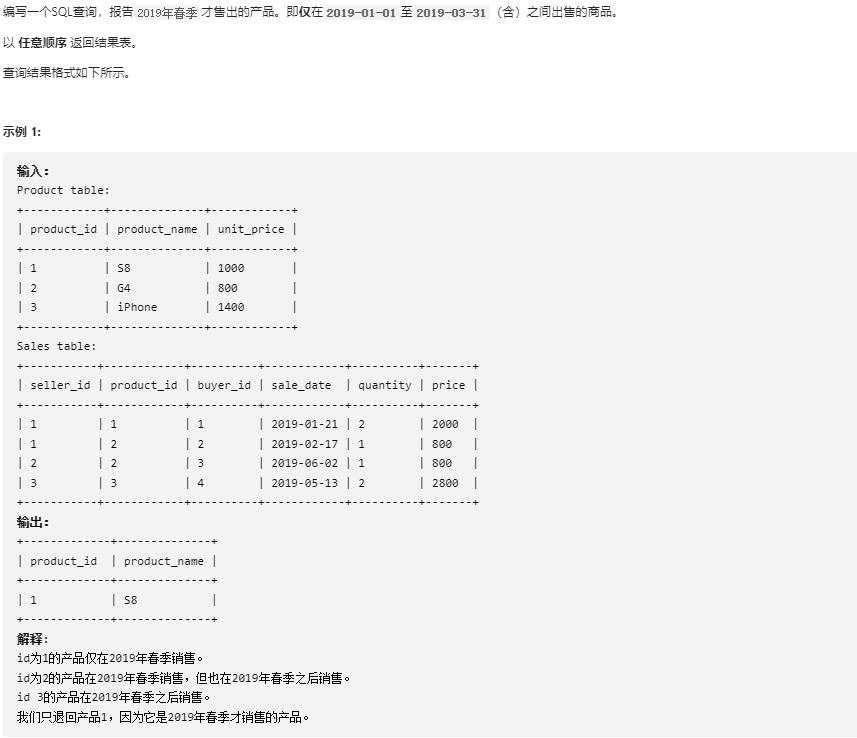
创建语句:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Create table If Not Exists Product (product_id int , product_name varchar (10 ), unit_price int );Create table If Not Exists Sales (seller_id int , product_id int , buyer_id int , sale_date date , quantity int , price int );Truncate table Product;insert into Product (product_id, product_name, unit_price) values ('1' , 'S8' , '1000' );insert into Product (product_id, product_name, unit_price) values ('2' , 'G4' , '800' );insert into Product (product_id, product_name, unit_price) values ('3' , 'iPhone' , '1400' );Truncate table Sales;insert into Sales (seller_id, product_id, buyer_id, sale_date, quantity, price) values ('1' , '1' , '1' , '2019-01-21' , '2' , '2000' );insert into Sales (seller_id, product_id, buyer_id, sale_date, quantity, price) values ('1' , '2' , '2' , '2019-02-17' , '1' , '800' );insert into Sales (seller_id, product_id, buyer_id, sale_date, quantity, price) values ('2' , '2' , '3' , '2019-06-02' , '1' , '800' );insert into Sales (seller_id, product_id, buyer_id, sale_date, quantity, price) values ('3' , '3' , '4' , '2019-05-13' , '2' , '2800' );
依次获得相关子表
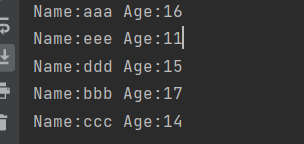
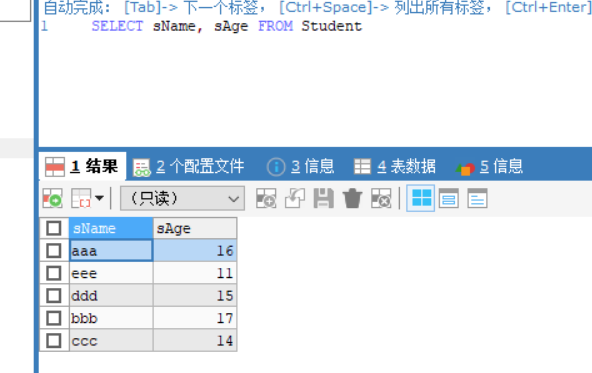
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 import java.sql.Connection;import java.sql.DriverManager;import java.sql.ResultSet;import java.sql.Statement;public class test public static final String URL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306" ; public static final String USER = "root" ; public static final String PASSWORD = "123456" ; public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" ); Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(URL, USER, PASSWORD); Statement stmt = conn.createStatement(); stmt.executeQuery("use mytest" ); ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery("SELECT sName, sAge FROM Student" ); while (rs.next()){ System.out.println("Name:" + rs.getString("sName" )+" Age:" +rs.getInt("sAge" )); } } }
加载驱动程序需要进行下载相关jar包,然后导入,
参考
Java MySQL 连接 | 菜鸟教程 (runoob.com)
(47条消息) 【IDEA】向IntelliJ IDEA创建的项目导入Jar包的两种方式_谙忆的博客-CSDN博客_idea如何添加jar包
其中rs.next()相当于跳过表头,逐行打印则需要循环rs.next(),结果为
对应表中数据
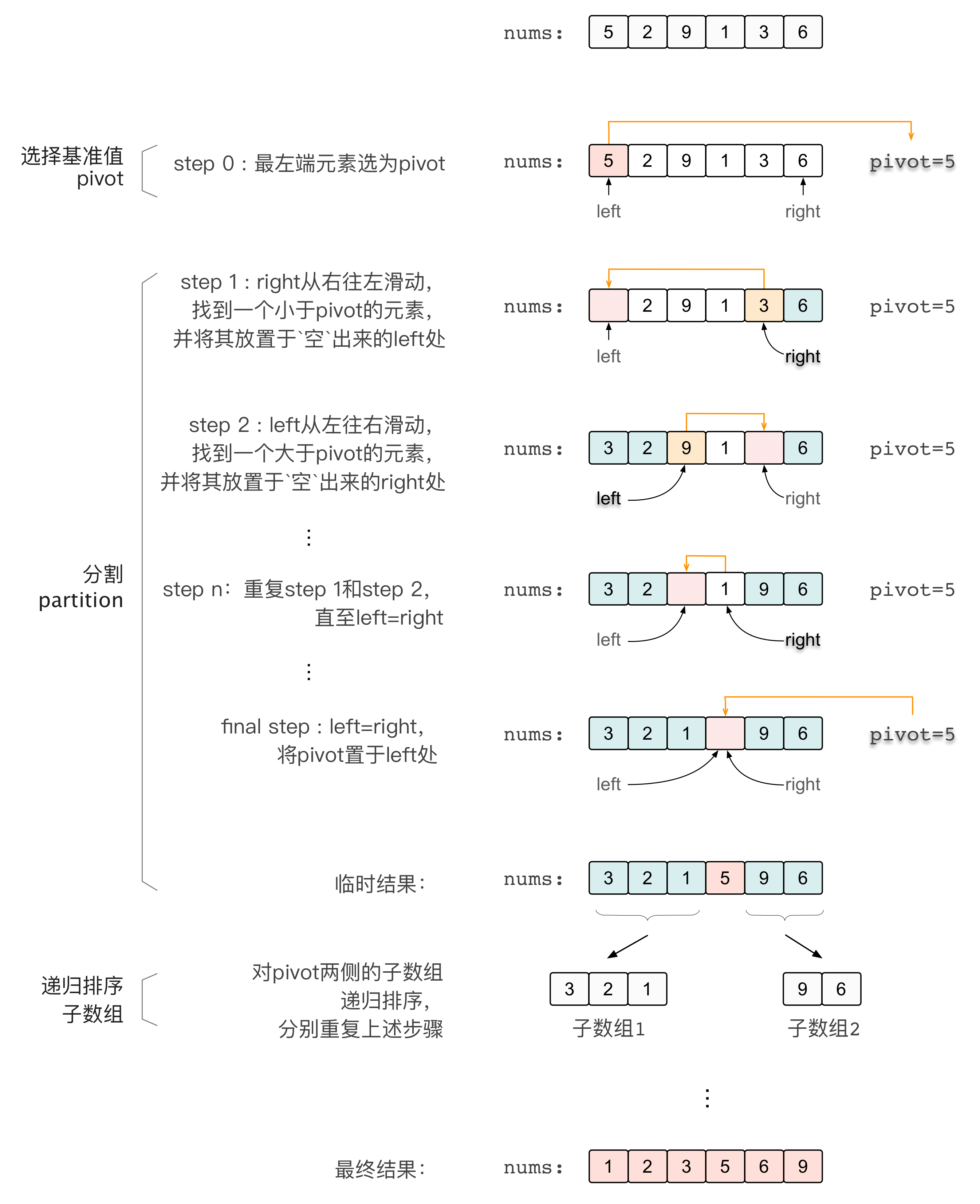
主要是分治思想,从大往下分,然后再合并
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 from typing import List class Solution : def merge (self, nums, mid, l, r ): tmp = [] i,j = l,mid+1 while (i <= mid or j <= r): if (nums[i] <= nums[j]): tmp.append(nums[i]) i += 1 if (i == mid + 1 ): tmp += nums[j:r + 1 ] break else : tmp.append(nums[j]) j += 1 if (j == r + 1 ): tmp += nums[i:mid + 1 ] break nums[l:r + 1 ] = tmp def mergeSort (self, nums, l, r ): if (l >= r): return mid = int ((l + r) / 2 ) self.mergeSort(nums, l, mid) self.mergeSort(nums, mid + 1 , r) self.merge(nums, mid, l, r) def sortArray (self, nums: List [int ] ) -> List [int ]: self.mergeSort(nums, 0 , len (nums) - 1 ) return nums
也是分治思想,双指针,参考『 3种排序一网打尽 』 快速排序、归并排序、堆排序详解 - 排序数组 - 力扣(LeetCode)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution : def partition (self, nums, low, high ): pivot_idx = random.randint(low,high) pivot = nums[pivot_idx] nums[low],nums[pivot_idx] = nums[pivot_idx],nums[low] left = low right = high while left < right: while (left < right and nums[right] >= pivot): right -= 1 nums[left] = nums[right] while (left < right and nums[left] <= pivot): left += 1 nums[right] = nums[left] nums[left] = pivot return left def quickSort (self, nums,low,high ): if (low >= high): return mid = self.partition(nums,low,high) self.quickSort(nums,low,mid-1 ) self.quickSort(nums,mid+1 ,high) def sortArray (self, nums: List [int ] ) -> List [int ]: self.quickSort(nums, 0 , len (nums) - 1 ) return nums
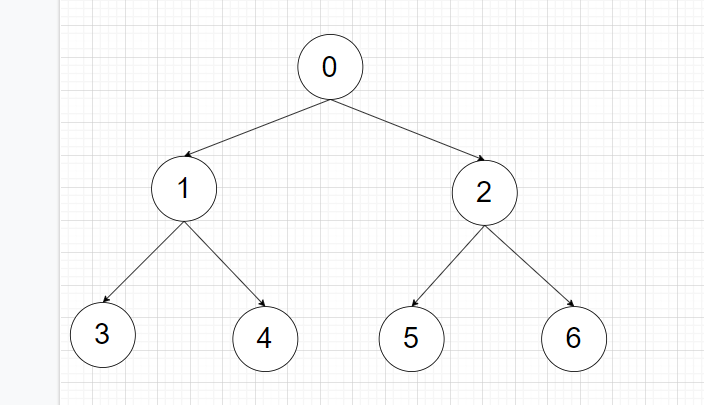
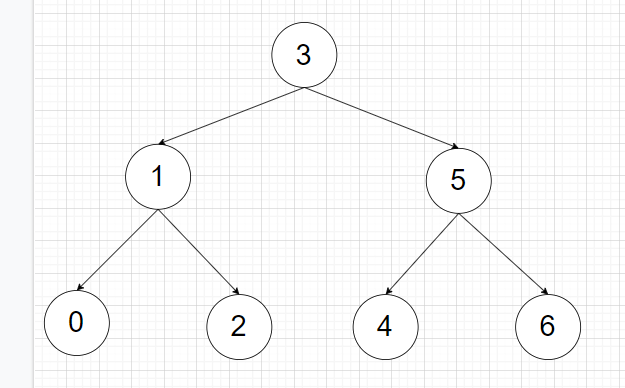
以下图为例子
先序遍历:首先访问根节点,然后访问左子树,最后访问右子树。
顺序为:0-1-3-4-2-5-6
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public void beforeTraverse (Node root) if (root == null ) return ; System.out.println(root.val); beforeTraverse(root.left); beforeTraverse(root.right); }
中序遍历:首先访问左子树,然后访问根结点,最后访问右子树。
顺序为:3-1-4-0-5-2-6
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public void beforeTraverse (Node root) if (root == null ) return ; beforeTraverse(root.left); System.out.println(root.val); beforeTraverse(root.right); }
后序遍历:首先访问左子树,然后访问右子树,最后访问根结点。
顺序为:3-4-1-5-6-2-0
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public void beforeTraverse (Node root) if (root == null ) return ; beforeTraverse(root.left); beforeTraverse(root.right); System.out.println(root.val); }
二叉查找树、二叉排序树
若它的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的值; 若它的右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值; 它的左、右子树也分别为二叉搜索树
以下图为例子
那么二叉搜索树的中序遍历即为递增序列:0-1-2-3-4-5-6
堆是一颗完全二叉树
要求排序时间算法复杂度为O(nlogn)常用堆排序
都是从idx最大的非叶子结点的子树开始,将不满足大(小)顶堆的子树递归进行下沉操作
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 void maxShiftDown (int * array , int rootIdx, int heapSize) int leftIdx = rootIdx * 2 + 1 ; int rightIdx = rootIdx * 2 + 2 ; int maxIdx = rootIdx; if ( leftIdx < heapSize && array [leftIdx] > array [maxIdx]){ maxIdx = leftIdx; } if ( rightIdx < heapSize && array [rightIdx] > array [maxIdx]){ maxIdx = rightIdx; } if ( maxIdx != rootIdx){ int tmp = array [rootIdx]; array [rootIdx] = array [maxIdx]; array [maxIdx] = tmp; maxShiftDown(array , maxIdx, heapSize); } } void buildMaxHeap (int * array ,int heapSize) for (int i = heapSize/2 ; i >= 0 ; i--){ maxShiftDown(array , i, heapSize); } } int main () int nums[27 ] = {3 ,2 ,3 ,1 ,2 ,4 ,5 ,5 ,6 ,7 ,7 ,8 ,2 ,3 ,1 ,1 ,1 ,10 ,11 ,5 ,6 ,2 ,4 ,7 ,8 ,5 ,6 }; buildMaxHeap(nums,27 ); return 0 ; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 void minShiftDown (int * array , int rootIdx, int heapSize) int leftIdx = rootIdx * 2 + 1 ; int rightIdx = rootIdx * 2 + 2 ; int minIdx = rootIdx; if ( leftIdx < heapSize && array [leftIdx] < array [minIdx]){ minIdx = leftIdx; } if ( rightIdx < heapSize && array [rightIdx] < array [minIdx]){ minIdx = rightIdx; } if (minIdx != rootIdx){ int tmp = array [rootIdx]; array [rootIdx] = array [minIdx]; array [minIdx] = tmp; minShiftDown(array , minIdx, heapSize); } } void buildMinHeap (int * array ,int heapSize) for (int i = heapSize/2 ; i >= 0 ; i--){ minShiftDown(array , i, heapSize); } } int main () int nums[27 ] = {3 ,2 ,3 ,1 ,2 ,4 ,5 ,5 ,6 ,7 ,7 ,8 ,2 ,3 ,1 ,1 ,1 ,10 ,11 ,5 ,6 ,2 ,4 ,7 ,8 ,5 ,6 }; buildMinHeap(nums,27 ); return 0 ; }
合起来加个flag即可决定大顶堆还是小顶堆了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 void shiftDown (int * array , int rootIdx, int heapSize, int flag) int leftIdx = rootIdx * 2 + 1 ; int rightIdx = rootIdx * 2 + 2 ; int chooseIdx = rootIdx; if (flag == 0 ){ if ( leftIdx < heapSize && array [leftIdx] < array [chooseIdx]){ chooseIdx = leftIdx; } if ( rightIdx < heapSize && array [rightIdx] < array [chooseIdx]){ chooseIdx = rightIdx; } } else { if ( leftIdx < heapSize && array [leftIdx] > array [chooseIdx]){ chooseIdx = leftIdx; } if ( rightIdx < heapSize && array [rightIdx] > array [chooseIdx]){ chooseIdx = rightIdx; } } if (chooseIdx != rootIdx){ int tmp = array [rootIdx]; array [rootIdx] = array [chooseIdx]; array [chooseIdx] = tmp; shiftDown(array , chooseIdx, heapSize, flag); } } void buildHeap (int * array ,int heapSize,int flag) for (int i = heapSize/2 ; i >= 0 ; i--){ shiftDown(array , i, heapSize,flag); } } int main () int nums[27 ] = {3 ,2 ,3 ,1 ,2 ,4 ,5 ,5 ,6 ,7 ,7 ,8 ,2 ,3 ,1 ,1 ,1 ,10 ,11 ,5 ,6 ,2 ,4 ,7 ,8 ,5 ,6 }; int heapSize = 27 ; buildHeap(nums,heapSize,0 ); return 0 ; }
一般只能删除堆顶元素
从删除堆顶元素,将堆尾部元素放到堆顶,然后下沉该元素
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 void shiftDown (int * array , int rootIdx, int heapSize, int flag) int leftIdx = rootIdx * 2 + 1 ; int rightIdx = rootIdx * 2 + 2 ; int chooseIdx = rootIdx; if (flag == 0 ){ if ( leftIdx < heapSize && array [leftIdx] < array [chooseIdx]){ chooseIdx = leftIdx; } if ( rightIdx < heapSize && array [rightIdx] < array [chooseIdx]){ chooseIdx = rightIdx; } } else { if ( leftIdx < heapSize && array [leftIdx] > array [chooseIdx]){ chooseIdx = leftIdx; } if ( rightIdx < heapSize && array [rightIdx] > array [chooseIdx]){ chooseIdx = rightIdx; } } if (chooseIdx != rootIdx){ int tmp = array [rootIdx]; array [rootIdx] = array [chooseIdx]; array [chooseIdx] = tmp; shiftDown(array , chooseIdx, heapSize, flag); } } int main () int nums[27 ] = {3 ,2 ,3 ,1 ,2 ,4 ,5 ,5 ,6 ,7 ,7 ,8 ,2 ,3 ,1 ,1 ,1 ,10 ,11 ,5 ,6 ,2 ,4 ,7 ,8 ,5 ,6 }; int heapSize = 27 ; buildHeap(nums,heapSize,0 ); nums[0 ] = nums[heapSize-1 ]; heapSize -= 1 ; shiftDown(nums,0 ,heapSize,0 ); return 0 ; }
总是在堆尾部插入元素,然后对该元素执行上浮操作
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 void shiftUp (int * array , int insertIdx,int flag) int parentIdx = 0 ; if (insertIdx == 0 ){ return ; } if (insertIdx % 2 == 0 ){ parentIdx = (insertIdx - 2 ) / 2 ; } else { parentIdx = (insertIdx - 1 ) / 2 ; } if (flag == 0 ){ if (array [parentIdx] > array [insertIdx]){ int tmp = array [insertIdx]; array [insertIdx] = array [parentIdx]; array [parentIdx] = tmp; shiftUp(array ,parentIdx,flag); } } else { if (array [parentIdx] < array [insertIdx]){ int tmp = array [insertIdx]; array [insertIdx] = array [parentIdx]; array [parentIdx] = tmp; shiftUp(array ,parentIdx,flag); } } } int main () int nums[27 ] = {3 ,2 ,3 ,1 ,2 ,4 ,5 ,5 ,6 ,7 ,7 ,8 ,2 ,3 ,1 ,1 ,1 ,10 ,11 ,5 ,6 ,2 ,4 ,7 ,8 ,5 ,6 }; int heapSize = 27 ; buildMinHeap(nums,heapSize); nums[0 ] = nums[heapSize-1 ]; heapSize -= 1 ; minShiftDown(nums,0 ,heapSize); nums[heapSize] = 0 ; shiftUp(nums,heapSize,1 ); return 0 ; }
依次取堆顶元素,然后执行下沉操作使得堆依旧满足大(顶)堆,即可自行决定升序还是降序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 void heapSort (int * array , int heapSize,int flag) for (int i = heapSize - 1 ; i >= 1 ; --i) { int tmp = array [i]; array [i] = array [0 ]; array [0 ] = tmp; heapSize -= 1 ; shiftDown(array , 0 , heapSize,flag); } }
在线演示BST网址:https://www.cs.usfca.edu/~galles/visualization/BST.html
主要是python
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 import syswhile True : line = sys.stdin.readline() if line == '' : break line = line.split(" " ) print (int (line[0 ])+int (line[1 ].replace("\n" ,"" )))

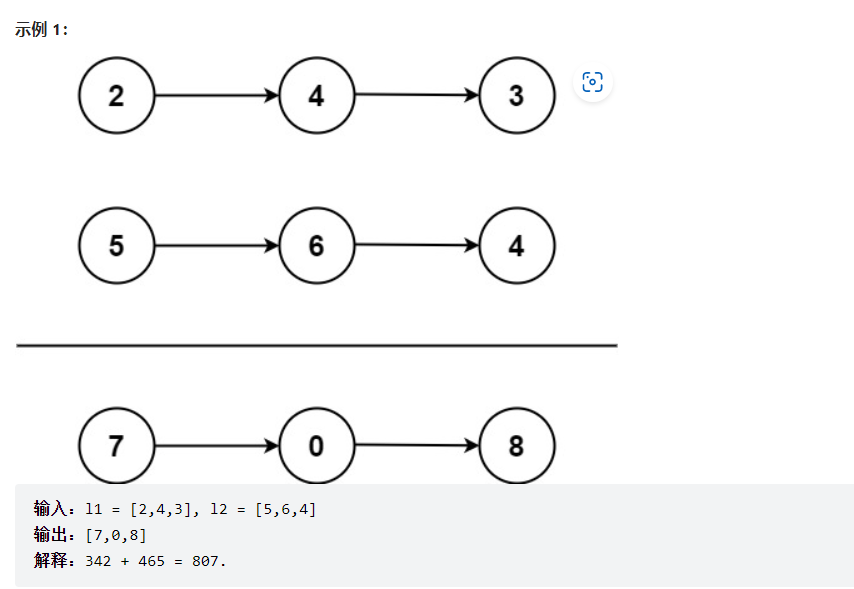

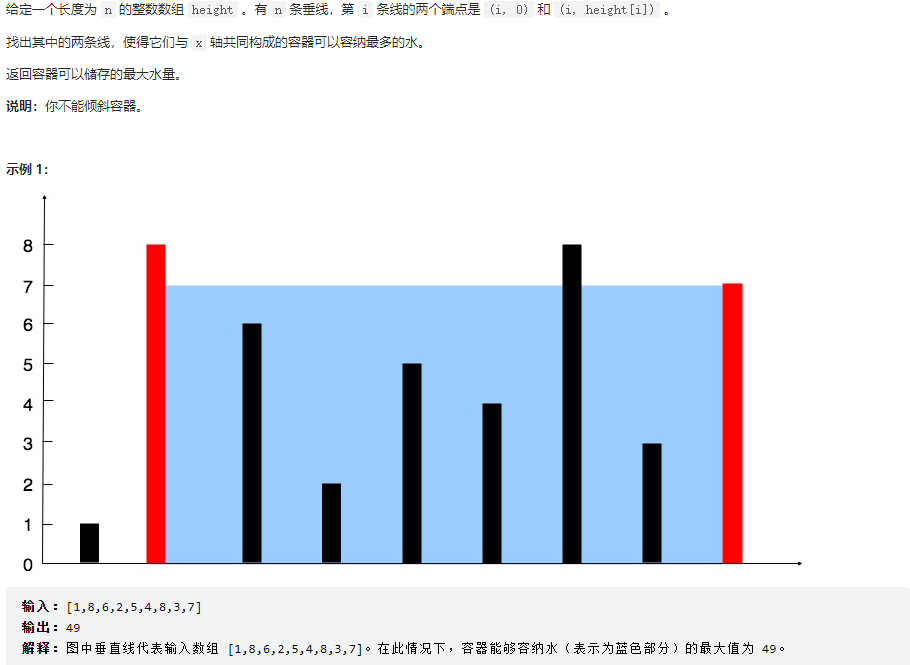
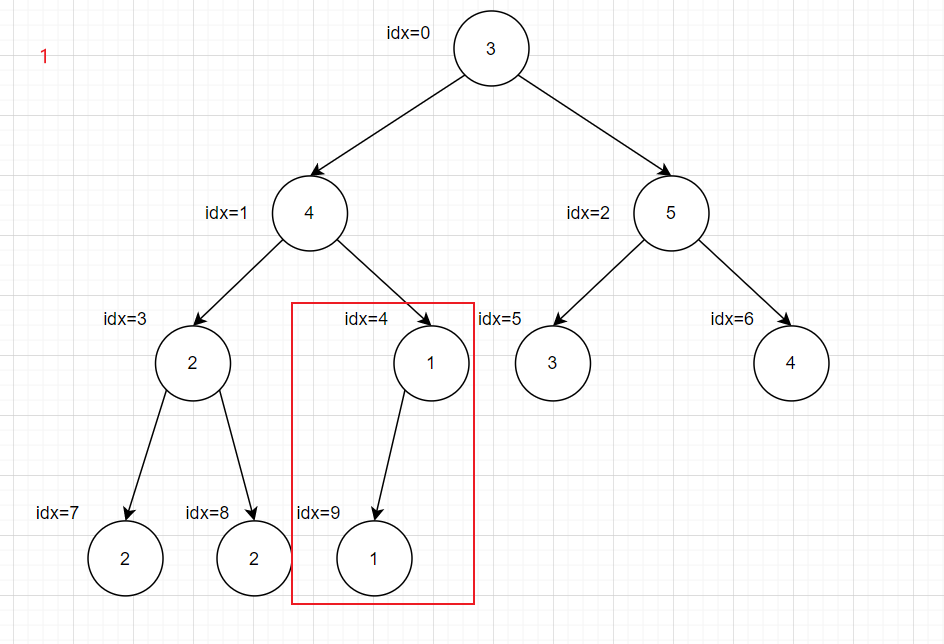
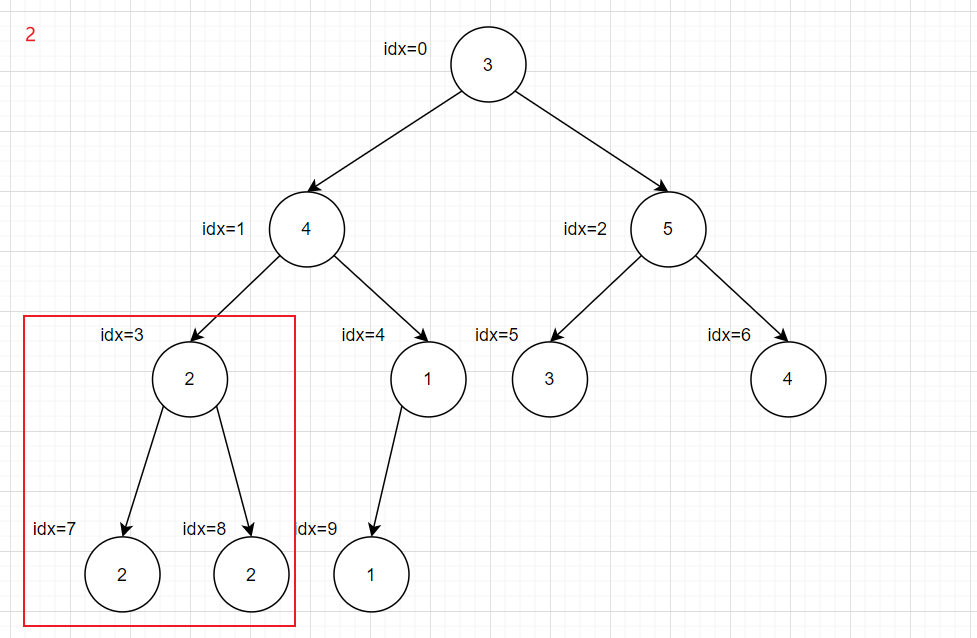
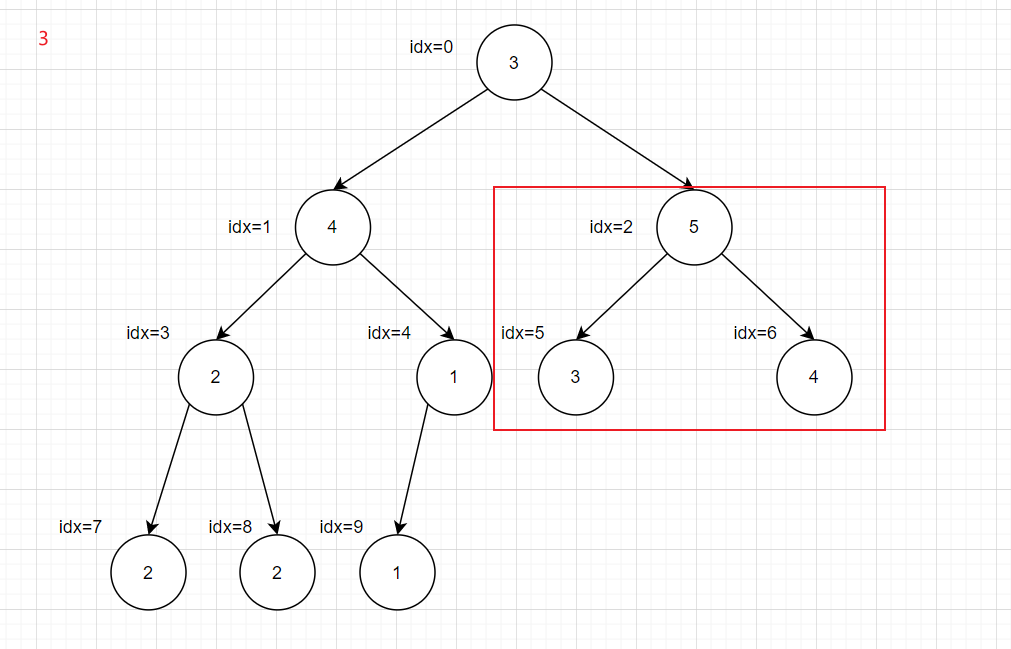
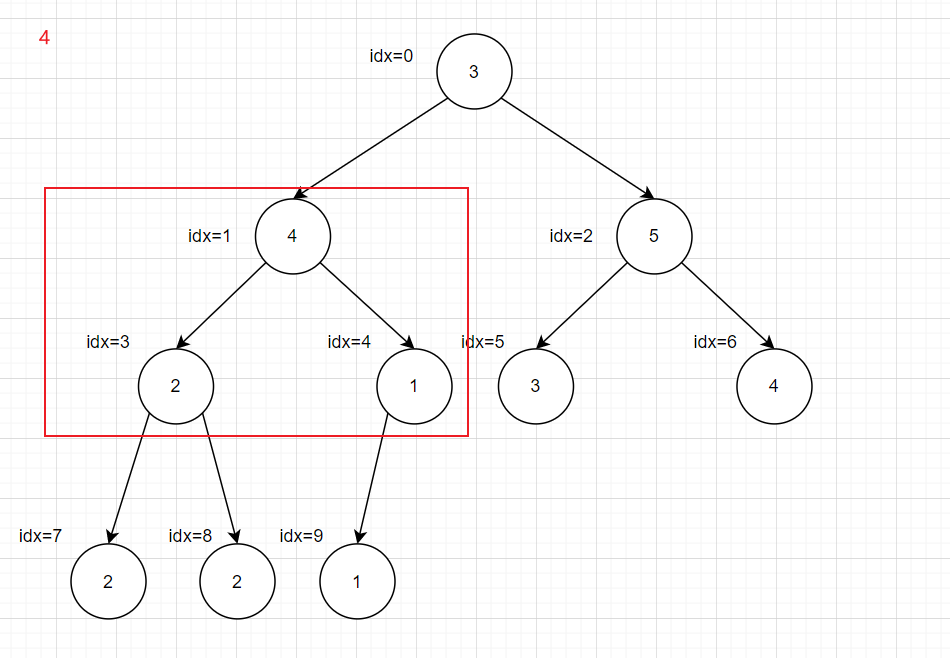
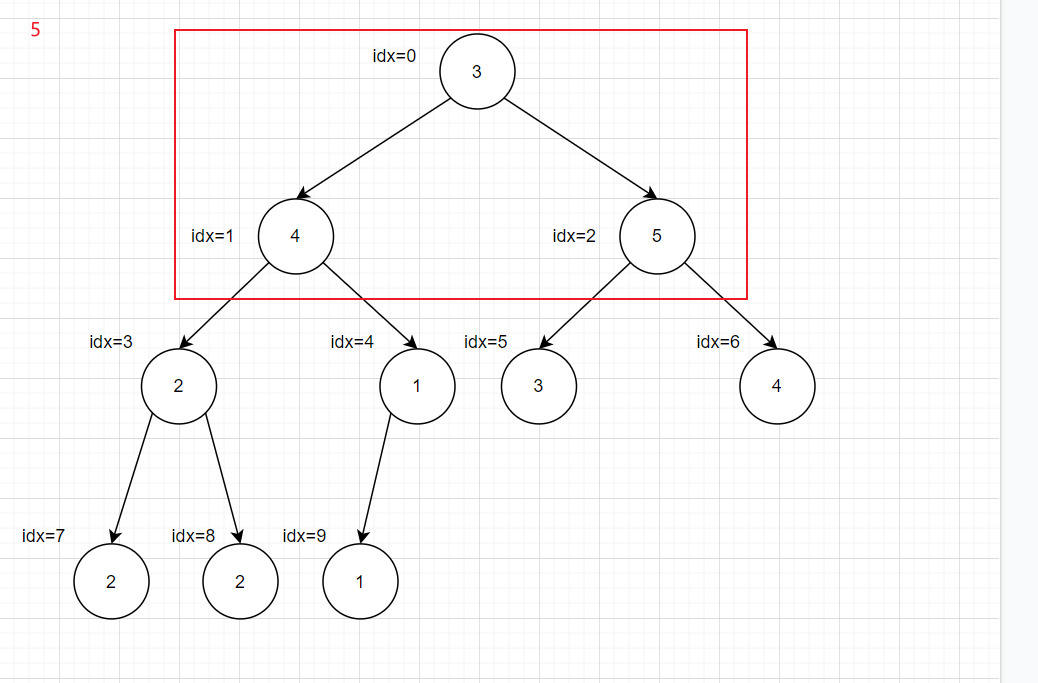
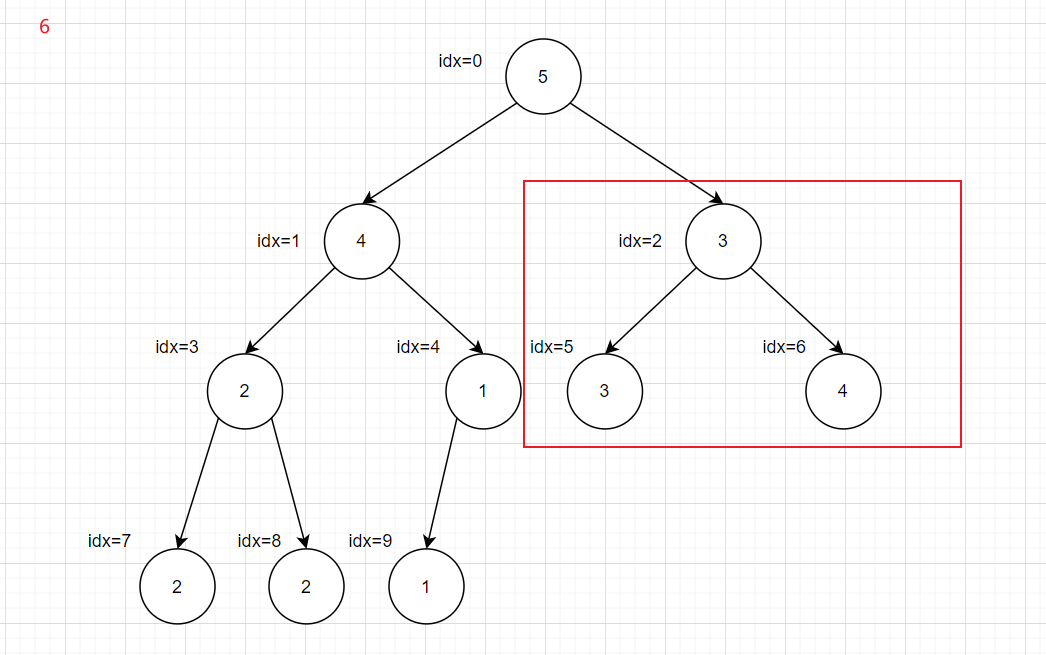
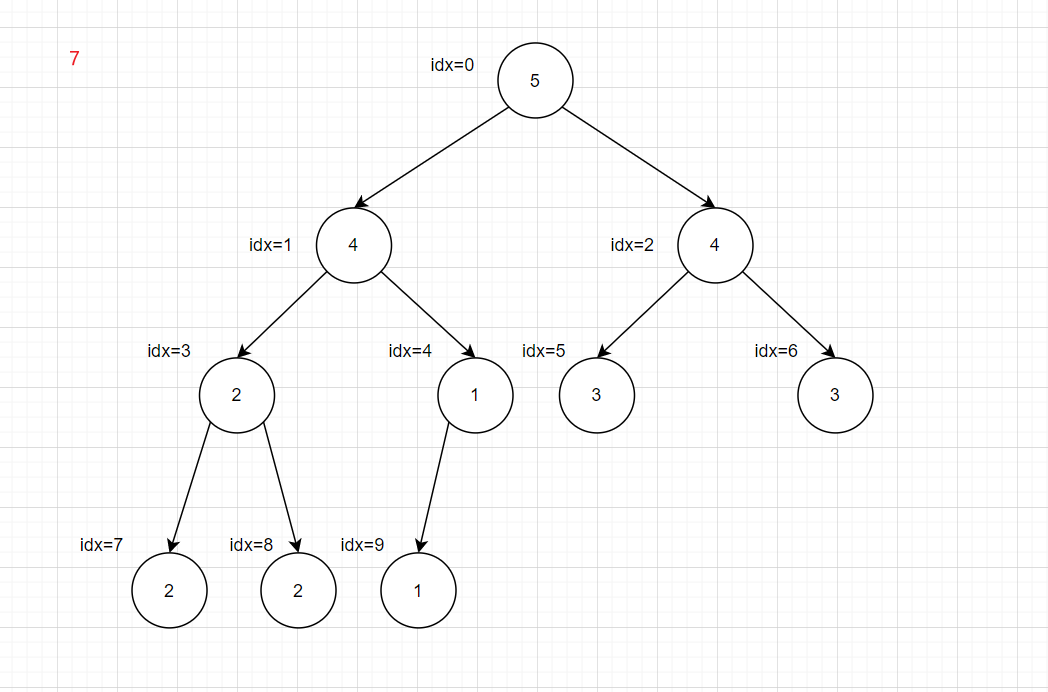





 递归会超时,所以转化为循环
递归会超时,所以转化为循环