1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 import angrp=angr.Project("./signal.exe" ) state=p.factory.entry_state() sm=p.factory.simgr(state) good=0x4017A5 fail=0x4017A5 sm.explore(find=good,avoid=fail) if sm.found: find_state=sm.found[0 ] print (find_state.posix.dumps(0 ))
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 import angrimport sysimport claripyfilePath = "/home/hacker/Desktop/Reverse/Angr/AngrCTF_FITM/" def Go (): path_to_binary = filePath + "./14_angr_shared_library/lib14_angr_shared_library.so" base = 0x4000000 project = angr.Project(path_to_binary, load_options={ 'main_opts' : {'custom_base_addr' : base} }) buffer_pointer = claripy.BVV(0x3000000 , 32 ) validate_function_address = base + 0x6d7 initial_state = project.factory.call_state(validate_function_address, buffer_pointer, claripy.BVV(8 , 32 )) password = claripy.BVS('password' , 8 *8 ) initial_state.memory.store(buffer_pointer, password) simulation = project.factory.simgr(initial_state) success_address = base + 0x783 simulation.explore(find=success_address) if simulation.found: for i in simulation.found: solution_state = i solution_state.add_constraints(solution_state.regs.eax != 0 ) solution = solution_state.solver.eval (password,cast_to=bytes ) print ("[+] Success! Solution is: {0}" .format (solution)) else : raise Exception('Could not find the solution' ) if __name__ == "__main__" : Go()
1 2 3 4 5 path_to_binary = filePath + "00_angr_find/00_angr_find" project = angr.Project(path_to_binary, auto_load_libs=False ) initial_state = project.factory.entry_state() simulation = project.factory.simgr(initial_state)
auto_load_libs:表是否载入依赖库的函数,libc等,如果不载入,返回的值是不可约束的,但是载入可能会路径爆炸。
initial_state:告诉angr从入口处开始,或者从指定的地址start_address开始,不过这样一般需要设置一下寄存器。
simulation:获取我们操作的对象,之后的操作即对这个对象进行操作。
1 2 print_good_address = 0x8048678 avoid_me_address = 0x080485A8
表如果程序到达print_good_address,即代表成功解题,一般题中就是输出flag的地址。
avoid_me_address则用在需要避免到达的地方
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 def is_successful (state ): stdout_output = state.posix.dumps(sys.stdout.fileno()) if b'Good Job.' in stdout_output: return True else : return False def should_abort (state ): stdout_output = state.posix.dumps(sys.stdout.fileno()) if b'Try again.' in stdout_output: return True else : return False
当程序中有多个正确输出的时候,获取程序输出,如果输出中包含标志性的符号Good Job,则代表成功到达,或者设置其他的标志性符号。或者当程序中有多个相同的错误输出的时候,获取程序输出,如果输出中包含标志性的符号Try Again,则代表应该需要避免的地方,而不用输入多个地址。
一般而言,可能输入的长度或者字符有些限制,比如scanf的格式化获取输入,这时候我们就可以通过向量生成限制性的输入字符,缩小搜索路径
1 2 3 4 5 import claripypasswd_size_in_bits = 32 passwd0 = claripy.BVS('passwd0' , passwd_size_in_bits) passwd1 = claripy.BVS('passwd1' , passwd_size_in_bits) passwd2 = claripy.BVS('passwd2' , passwd_size_in_bits)
设置了三个向量,长度为32bit
BVS():代表位向量创建
FPS():代表符号向量创建
当程序有时候不需要从头开始,而是只测试某个地方或者在某个地方需要更改寄存器时,可以进行设置
1 2 3 4 initial_state.regs.eax = passwd0 initial_state.regs.ebx = passwd1 initial_state.regs.edx = passwd2
1 2 initial_state.regs.ebp = initial_state.regs.esp *
比如如下情形,需要0x8的栈空间
那么先将esp放到ebp-0x8的位置
1 2 3 padding_length_in_bytes = 0x08 initial_state.regs.esp -= padding_length_in_bytes
然后设置向量,压入栈中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 passwd0 = claripy.BVS('var_10' , 32 ) passwd1 = claripy.BVS('var_C' , 32 ) initial_state.stack_push(passwd0) initial_state.stack_push(passwd1)
这样即可完成栈中数据的布置
这里符号化栈上数据时,只能一个一个push,即32位一次push进4字节,64位一次push进8字节,不能多,不然会造成符号截断。这里其实可以直接通过获取rsp,然后利用rsp来加载数据即可。
1 2 3 4 initial_state.regs.rsp = initial_state.regs.rbp buf_addr = initial_state.regs.rsp - 0x10 passwd0 = claripy.BVS('password' , 0x8 * 8 ) initial_state.memory.store(buf_addr, passwd0)
寻址需要符号化的内存地址,如下:
即符号化四个八字节长度的user_input
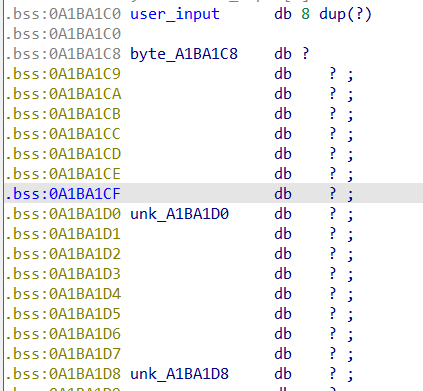
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 passwd_size_in_bits = 64 passwd0 = claripy.BVS('passwd0' , passwd_size_in_bits) passwd1 = claripy.BVS('passwd1' , passwd_size_in_bits) passwd2 = claripy.BVS('passwd2' , passwd_size_in_bits) passwd3 = claripy.BVS('passwd3' , passwd_size_in_bits) passwd0_address = 0xA1BA1C0 initial_state.memory.store(passwd0_address, passwd0) initial_state.memory.store(passwd0_address + 0x8 , passwd1) initial_state.memory.store(passwd0_address + 0x10 , passwd2) initial_state.memory.store(passwd0_address + 0x18 , passwd3)
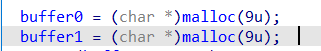
即在buffer0和buffer1中保存的是malloc出来的内存指针
这样我们就可以向这两个buf中写入内存地址,然后把需要符号化的内存写入到对应的内存地址中,这里选取的内存地址设置为
1 2 fake_heap_address0 = 0xffffc93c fake_heap_address1 = 0xffffc94c
最终如下设置
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 fake_heap_address0 = 0xffffc93c pointer_to_malloc_memory_address0 = 0xabcc8a4 fake_heap_address1 = 0xffffc94c pointer_to_malloc_memory_address1 = 0xabcc8ac initial_state.memory.store(pointer_to_malloc_memory_address0, fake_heap_address0, endness=project.arch.memory_endness) initial_state.memory.store(pointer_to_malloc_memory_address1, fake_heap_address1, endness=project.arch.memory_endness) initial_state.memory.store(fake_heap_address0, passwd0) initial_state.memory.store(fake_heap_address1, passwd1)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 filename = 'OJKSQYDP.txt' symbolic_file_size_bytes = 64 passwd0 = claripy.BVS('password' , symbolic_file_size_bytes * 8 ) passwd_file = angr.storage.SimFile(filename, content=passwd0, size=symbolic_file_size_bytes) initial_state.fs.insert(filename, passwd_file)
当在循环里进行比较判断是,会产生很多分支
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 _BOOL4 __cdecl check (int a1, unsigned int a2) int v3; unsigned int i; v3 = 0 ; for ( i = 0 ; i < a2; ++i ) { if ( *(_BYTE *)(i + a1) == *(_BYTE *)(i + 0x804A040 ) ) ++v3; } return v3 == a2; }
这里的a2=16,即将16个字符都拿出来逐个比较,每次比较产生两个分支,16次比较就会产生2^16=65536个分支,会使得分支变得很大,但是这里其实只是一个比较函数,保证a1代表字符串的内容和0x804A040中保存的字符串内容相等就可以了,这里就可以运行到该函数之前,然后自己获取对应内存中值进行比较,添加限制即可。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 buff_addr = 0x0804A050 address_to_check_constraint = 0x08048565 simulation = project.factory.simgr(initial_state) simulation.explore(find=address_to_check_constraint) if simulation.found: solution_state = simulation.found[0 ] constrained_parameter_address = buff_addr constrained_parameter_size_bytes = 16 constrained_parameter_bitvector = solution_state.memory.load(constrained_parameter_address,constrained_parameter_size_bytes) constrained_parameter_desired_value = 'AUPDNNPROEZRJWKB' solution_state.solver.add(constrained_parameter_bitvector == constrained_parameter_desired_value) solution0 = solution_state.solver.eval (passwd0,cast_to=bytes )
即用自己编写的函数替代程序中的函数来执行,假设这里想hook掉以下函数,该函数即为之前的比较函数check
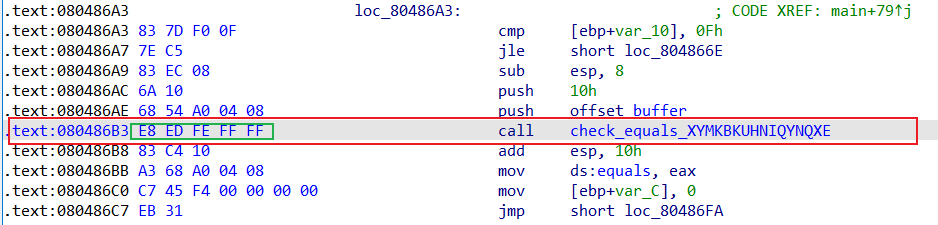
那么看字节码可知对应的函数为5个字节,地址为0x80486B3
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 check_equals_called_address = 0x80486B3 instruction_to_skip_length = 5 @project.hook(check_equals_called_address, length=instruction_to_skip_length ) def skip_check_equals_ (state ): user_input_buffer_address = 0x804A054 user_input_buffer_length = 16 user_input_string = state.memory.load( user_input_buffer_address, user_input_buffer_length, endness=archinfo.Endness.LE ) check_against_string = 'XKSPZSJKJYQCQXZV' register_size_bit = 32 state.regs.eax = claripy.If( user_input_string == check_against_string, claripy.BVV(1 , register_size_bit), claripy.BVV(0 , register_size_bit) )
当函数被调用了多次,而我们又需要对每一个这个函数进行hook时,就可以通过函数名进行hook
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 _BOOL4 __cdecl check_equals_ORSDDWXHZURJRBDH (char *to_check, unsigned int length) int v3; unsigned int i; v3 = 0 ; for ( i = 0 ; i < length; ++i ) { if ( to_check[i] == *(_BYTE *)(i + 0x804C048 ) ) ++v3; } return v3 == length; }
比如替换上述的函数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class ReplacementCheckEquals (angr.SimProcedure ): def run (self, to_check, length ): user_input_buffer_address = to_check user_input_buffer_length = length user_input_string = self.state.memory.load( user_input_buffer_address, user_input_buffer_length) check_against_string = 'ORSDDWXHZURJRBDH' return claripy.If( user_input_string == check_against_string, claripy.BVV(1 , 32 ), claripy.BVV(0 , 32 )) check_equals_symbol = 'check_equals_ORSDDWXHZURJRBDH' project.hook_symbol(check_equals_symbol, ReplacementCheckEquals())
主要就是定义一个类,将所有函数名称为check_equals_ORSDDWXHZURJRBDH的函数用类ReplacementCheckEquals中的run函数替换
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class ReplacementScanf (angr.SimProcedure ): def run (self, format_string, param0, param1 ): scanf0 = claripy.BVS('scanf0' , 32 ) scanf1 = claripy.BVS('scanf1' , 32 ) scanf0_address = param0 self.state.memory.store(scanf0_address, scanf0, endness=project.arch.memory_endness) scanf1_address = param1 self.state.memory.store(scanf1_address, scanf1, endness=project.arch.memory_endness) self.state.globals ['solutions' ] = (scanf0, scanf1) scanf_symbol = '__isoc99_scanf' project.hook_symbol(scanf_symbol, ReplacementScanf())
当程序使用静态编译时,可能需要Hook一些静态库函数
在探索开始之前添加即可
1 2 3 4 project.hook(0x804ed40 , angr.SIM_PROCEDURES['libc' ]['printf' ]()) project.hook(0x804ed80 , angr.SIM_PROCEDURES['libc' ]['scanf' ]()) project.hook(0x804f350 , angr.SIM_PROCEDURES['libc' ]['puts' ]()) project.hook(0x8048d10 , angr.SIM_PROCEDURES['glibc' ]['__libc_start_main' ]())
当程序对于flag的加解密处理函数在外部库中时,这时候可以直接调用外部库中的函数进行符号执行
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 base = 0x4000000 project = angr.Project(path_to_binary, load_options={ 'main_opts' : {'custom_base_addr' : base} }) buffer_pointer = claripy.BVV(0x3000000 , 32 ) validate_function_address = base + 0x6d7 initial_state = project.factory.call_state(validate_function_address, buffer_pointer, claripy.BVV(8 , 32 )) password = claripy.BVS('password' , 8 *8 ) initial_state.memory.store(buffer_pointer, password)
main_opts为主程序指定加载参数,常用以下参数
custom_base_addr —— 使用的基地址
custom_entry_point —— 使用的入口点
custom_arch —— 使用的处理器体系结构的名字
这样在之后的设置成功地址也需要用到base
1 success_address = base + 0x783
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 def hook_Normal (state ): state.regs.rax = 8 p.hook(0x40168e , hook_Normal, length=5 ) p.hook_symbol('ptrace' , angr.SIM_PROCEDURES['stubs' ]['ReturnUnconstrained' ](return_value=0 )) def patch_0 (state ): pass
1 simulation.explore(find=is_successful, avoid=should_abort)
simulation.explore表开始探索,试图进入到print_good_address中
该模式可以对路径爆炸进行一些解决
https://www.anquanke.com/post/id/251984
但是在需要探索所有路径的时候,veritesting会出错,将一些路径合并,从而无法抵达正确的deadend路径,详见csaw_wyvern/wyvern
1 simulation = project.factory.simgr(initial_state, veritesting=True )
1 2 3 4 5 6 if simulation.found: solution_state = simulation.found[0 ] solution = solution_state.posix.dumps(sys.stdin.fileno()) print ("[+] Success! Solution is: {}" .format (solution.decode("utf-8" ))) else : raise Exception('Could not find the solution' )
即获取找到的第一串符号,然后输出
这个一般在最开始使用位向量BVS创建输入的时候使用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 if simulation.found: for solution_state in simulation.found: solution0 = format (solution_state.solver.eval (passwd0), 'x' ) solution1 = format (solution_state.solver.eval (passwd1), 'x' ) solution2 = format (solution_state.solver.eval (passwd2), 'x' ) solution = solution0 + " " + solution1 + " " + solution2 print ("[+] Success! Solution is: {}" .format (solution)) else : raise Exception('Could not find the solution' )
输出的是十六进制的数字
接口
描述
solver.eval(expression)将会解出一个可行解
solver.eval_one(expression)将会给出一个表达式的可行解,若有多个可行解,则抛出异常
solver.eval_upto(expression, n)将会给出最多n个可行解,如果不足n个就给出所有的可行解。
solver.eval_exact(expression, n)将会给出n个可行解,如果解的个数不等于n个,将会抛出异常。
solver.min(expression)给出最小可行解
solver.max(expression)给出最大可行解
Stash: active 、deadend 、found等
基本块的区分通常以call,cmp-jz/jmp...,ret等为标志。
每次向前运行一个基本块,并返回进行分类
让 stash 中的所有状态都执行一个基本块,默认的 stash 为 active
每次向前运行一个基本块,并返回进行分类
根据find和avoid进行基本块的执行,最后会返回found和avoid状态
直接对应使用,不用添加其他的什么配置
1 state.regs.r0 = concrete_addr
文件在”/home/hacker/Desktop/Reverse/Angr/myTest/callBinaryFunc”
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 myFunc_addr = base + 0x64A project = angr.Project(path_to_binary, auto_load_libs=True ) prototype = SimTypeFunction((SimTypeInt(False ),SimTypeInt(False )),SimTypeInt(False )) myFunc = project.factory.callable (myFunc_addr, cc=project.factory.cc(func_ty=prototype), toc=None , concrete_only=True ) myFunc.perform_call(0 ,0x100 ) state = myFunc.result_state print (state.regs.rax)
或者如下:
1 func = project.factory.callable(project.loader.find_symbol('myFunc).rebased_addr)
只能从最开始进行
由于angr是只实现了C库,为了深入C++标准库中,我们需要在设置state时需要使用full_init_state方法,并且设置unicorn引擎
unicorn引擎可能可以加快运行速度,有时候也会放慢速度,就比如在只有一条路径,但是需要添加flag约束的:asisctffinals2015_fake
1 2 3 4 5 initial_state = project.factory.full_init_state( args=path_to_binary, add_options=angr.options.unicorn, stdin=flag, )
这种从最开始执行的方法通常用在路径分支不多的时候,如果比较多就容易路径爆炸。
将二进制文件加载到虚拟的地址空间
在加载二进制文件时可以设置特定的参数,使用 main_opts 和 lib_opts 参数进行设置。
backend - 指定 backendbase_addr - 指定基址entry_point - 指定入口点arch - 指定架构
1 2 >>> angr.Project('examples/fauxware/fauxware' , main_opts={'backend' : 'blob' , 'arch' : 'i386' }, lib_opts={'libc.so.6' : {'backend' : 'elf' }})<Project examples/fauxware/fauxware>
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 obj = proj.loader.main_object obj = proj.loader.all_objects obj.sections obj.plt obj.linked_base obj.mapped_base obj.max_addr
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 malloc = proj.loader.find_symbol('malloc' ) malloc = proj.loader.main_object.get_symbol('malloc' ) >>> malloc.malloc.is_common malloc.is_local malloc.owner_obj malloc.resolvedby malloc.is_export malloc.is_static malloc.rebased_addr malloc.size malloc.is_extern malloc.is_weak malloc.relative_addr malloc.subtype malloc.is_forward malloc.linked_addr malloc.resolve( malloc.type malloc.is_function malloc.name malloc.resolve_forwarder( malloc.is_import malloc.owner malloc.resolved >>> malloc.rebased_addr0x10002c0 >>> malloc.linked_addr 0x2c0 >>> malloc.relative_addr0x2c0
选项
auto_load_libs是否自动加载程序的依赖
skip_libs避免加载的库
except_missing_libs无法解析共享库时是否抛出异常
force_load_libs强制加载的库
ld_path共享库的优先搜索搜寻路径
信息
1 2 3 4 5 6 >>> proj = angr.Project('/bin/true' )>>> proj.loader.shared_objectsOrderedDict([('true' , <ELF Object true, maps [0x400000 :0x60721f ]>), ('libc.so.6' , <ELF Object libc-2.27 .so, maps [0x1000000 :0x13f0adf ]>), ('ld-linux-x86-64.so.2' , <ELF Object ld-2.27 .so, maps [0x2000000 :0x222916f ]>)]) >>> proj = angr.Project('/bin/true' , load_options={"auto_load_libs" : False })>>> proj.loader.shared_objectsOrderedDict([('true' , <ELF Object true, maps [0x400000 :0x60721f ]>)])
1 2 3 4 >>> angr.procedures.libc.malloc<module 'angr.procedures.libc.malloc' from '/home/angr/angr-dev/angr/angr/procedures/libc/malloc.py' > >>> angr.SIM_PROCEDURES['libc' ]['malloc' ]<class 'angr .procedures .libc .malloc .malloc '>
查看hook相关的信息
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 >>> stub_func = angr.SIM_PROCEDURES['stubs' ]['ReturnUnconstrained' ] >>> proj.hook(0x10000 , stub_func()) >>> proj.is_hooked(0x10000 ) True >>> proj.hooked_by(0x10000 )<ReturnUnconstrained> >>> proj.unhook(0x10000 )>>> @proj.hook(0x20000 , length=5 )... def my_hook (state ):... state.regs.rax = 1 >>> proj.is_hooked(0x20000 )True
1 sudo docker run -it --rm -v $PWD/myTest:/myTest angr/angr
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 import angrimport loggingproject = angr.Project("/myTest/callBinaryFunc" ) initial_state = project.factory.entry_state(add_options=angr.options.unicorn) logging.getLogger('angr' ).setLevel(logging.INFO) hex (initial_state.addr)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 import logginglogging.getLogger('angr' ).setLevel(logging.INFO) def hook (l=None ): if l: locals ().update(l) import IPython IPython.embed(banner1='' ,confirm_exit=False ) exit(0 ) hook(locals ())
或者使用ipdb
1 2 3 4 import ipdbipdb.set_trace()
使用手册
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 h(help):帮助命令 s(step into):进入函数内部 n(next):执行下一行 b(break): b line_number 打断点 cl(clear): 清除断点 c(continue): 一直执行到断点 r(return): 从当前函数返回 j(jump): j line_number,跳过代码片段,直接执行指定行号所在的代码 l(list): 列出上下文代码 a(argument): 列出传入函数所有的参数值 p/pp: print 和 pretty print 打印出变量值 r(restart): 重启调试器 q(quit): 推出调试,清除所有信息
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 sm = project.factory.simulation_manager() sm.run() initial_state = project.factory.blank_state(addr=start_address) simulation = project.factory.simgr(initial_state,veritesting=True ) simulation.explore(find=success_address)
以下为运行之后可能的状态路径
然后即可通过状态来查看当前状态的中的各种内存,寄存器等
1 2 3 block = state.block() block.capstone.pp()
一般而言,core可以从gdb中获得,得到当前gdb状态的所有数据,包括加载的libc函数等,我们就可以中获得相关的数据来初始化我们的state
然后就可以对应调试了,设置还是一样的设置,只不过地址直接变成当前的gdb中的地址即可。可以看到所有内存基本一致,只有rbp,rsp等栈指针不太一样,这样比较方便我们来获取数据调试。
当使用过的simulation想接着某个状态继续探索时,直接使用以下代码不会成功
1 simulation.explore(find = addr)
这时候需要获取当前simulation的状态state,然后依据该状态state新建一个newSimulation才能继续探索
1 2 3 4 def nextFind (project,state,find=0 ,avoid=0 ): simulation = project.factory.simgr(state,veritesting=True ) simulation.explore(find = find,avoid = avoid) return simulation
▲TIPS
1 2 3 4 p.factory.simulation_manager?
1.获取字符串
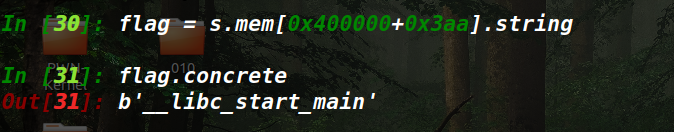
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 flag = state.mem[addr].string flag.concrete sm.deadended[1 ].posix.stdout.concretize()
1 2 3 4 a = claripy.BVV(0xffffffff , 0x4 *8 ) s = claripy.Solver() if (s.eval (a, 0 )[0 ] == 0xffffffff ): print ("Get!" )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 state = proj.factory.entry_state() state.regs.rax += state.mem[state.regs.rsp + 8 ].uint64_t.resolved result = simgr.found[0 ].memory.load(flag_addr, 40 ) simulation.found[0 ].solver.eval (result.get_bytes(0 ,0x17 ),cast_to=bytes )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 initial_state = p.factory.entry_state(args=[binary,argv1]) simgr = p.factory.simgr(inital_state,veritesting=True ) found = simgr.found[0 ] found.solver.eval (argv1,cast_to=bytes ) data = claripy.BVS('data' ,20 *8 ) p = angr.Project(path_to_binary, auto_load_libs=True ) inital_state = p.factory.entry_state(stdin=data) simgr = p.factory.simgr(inital_state,veritesting=True ) print (simgr.found[0 ].posix.stdin.concretize())
claripy.Concat方法用于bitVector的连接
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 flag_chars = claripy.BVS('flag_%d' % 1 , 8 ) flag = claripy.Concat(flag_chars + claripy.BVV(b'\n' )) flag_chars = [claripy.BVS('flag_%d' % i, 8 ) for i in range (28 )] flag = claripy.Concat(*flag_chars + [claripy.BVV(b'\n' )])
1 found.add_constraints(found.memory.load(flag_addr, 5 ) == int (binascii.hexlify(b"ASIS{" ), 16 ))
当输入某个数字,经过计算打印flag,只有简单几条路径时,就需要对flag进行约束才能正常输出,asisctffinals2015_fake
添加约束的时候,不能使用eval求解,只能使用load
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 flag = found.memory.load(flag_addr, 40 ) for i in range (5 , 5 +32 ): cond_0 = flag.get_byte(i) >= ord ('0' ) cond_1 = flag.get_byte(i) <= ord ('9' ) cond_2 = flag.get_byte(i) >= ord ('a' ) cond_3 = flag.get_byte(i) <= ord ('z' ) cond_4 = found.solver.And(cond_0, cond_1) cond_5 = found.solver.And(cond_2, cond_3) cond_6 = flag.get_byte(i) == ord ('-' ) cond_7 = flag.get_byte(i) == ord ('_' ) found.add_constraints(found.solver.Or(cond_4, cond_5,cond_6,cond_7)) found.add_constraints(flag.get_byte(32 +5 ) == ord ('}' ))
1 2 for b in arg1.chop(8 ): initial_state.add_constraints(b != 0 )
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 for i in range (36 ): state.add_constraints(flag.get_byte(i) >= 0x20 ) state.add_constraints(flag.get_byte(i) <= 0x7e ) for i in range (dataLen): state.solver.add( claripy.Or( *(data.get_byte(i) == x for x in printable) ) )
1 2 found.add_constraints(found.memory.load(flag_addr, 5 ) == int (binascii.hexlify(b"ASIS{" ), 16 )) found.add_constraints(flag.get_byte(32 +5 ) == ord ('}' ))
1 2 3 4 5 6 state.regs.rbp = state.regs.rsp state.mem[state.regs.rbp - 0x74 ].uint32_t = 0x40 state.mem[state.regs.rbp - 0x70 ].uint64_t = 0x1000 state.mem[state.regs.rbp - 0x68 ].uint64_t = 0x1008 state.mem[state.regs.rbp - 0x60 ].uint64_t = 0x1010 state.mem[state.regs.rbp - 0x58 ].uint64_t = 0x1018
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 print (sm.deadended[0 ].posix.stdout.concretize())out = b'' for pp in simulation.deadended: out = pp.posix.dumps(1 ) if b'flag{' in out: final_flag = next (filter (lambda s: b'flag{' in s, out.split())) print ("[+] Success! Solution is: {0}" .format (final_flag))
strtol(),strlen()等一系列的字符串操作
有时候会向量设置,最好在末尾加上’\x00’,使得某些情况能够通过。同样的当有canary的时候,没办法从压入canary的地方开始的时候,这时候最好给canary向量化或者给’\x00’截断。sym-write
同样的,在很多时候,最好加上{angr.options.SYMBOLIC_WRITE_ADDRESSES}选项,这个其实也不是很清楚,有的题不加也可以,但是有的题不加就不行。
1 state = project.factory.entry_state(add_options={angr.options.SYMBOLIC_WRITE_ADDRESSES})
x86的32位程序下,参数从栈上取,有时候通常需要设置这个才行的flareon2015_2
1 2 3 4 s.memory.store(s.regs.esp+12 , s.solver.BVV(50 ,8 *4 )) s.mem[s.regs.esp+8 ].uint32_t = 0x402159 s.mem[s.regs.esp+4 ].uint32_t = 0x4010e4 s.mem[s.regs.esp].uint32_t = 0x401064
正常情况下某个 state 被发现是不可满足条件的,那么state会进行回溯,来确定到底是哪个state不被满足,之后所有的state会被放入到stash中。但是有的时候回溯并不好,会比较不容易出结果,尤其是运算量比较大的时候,这时候就可以添加LAZY_SOLVES,不进行检查,先把所有路径跑完。
总的来说LAZY_SOLVES是在路径爆炸和花费在约束求解上的时间之间的平衡。
同样的,有的版本是默认开启,有的是默认关闭,对应修改即可
1 2 state = p.factory.blank_state(addr=START_ADDR, add_options={angr.options.LAZY_SOLVES}) state = p.factory.blank_state(addr=START_ADDR, remove_options={angr.options.LAZY_SOLVES})
详见题目google2016_unbreakable_1
比较适用于当find路径和avoid路径都比较容易抵达的时候,即某些库函数调用比较少,但是运算量比较庞大的时候,类似如下全是运算的
https://docs.angr.io/appendix/options#option-sets
day1-r1-a-1.pdf (hitcon.org)
https://flagbot.ch/lesson5.pdf
正常的angr只能执行.text段的代码,但是有的题会执行非.text段的代码,不过需要在创建Project的时候加入选项support_selfmodifying_code=True,详见题目tumctf2016_zwiebel
1 project = angr.Project("zwiebel" , support_selfmodifying_code=True )
设定n,表示从state的状态开始运行3个基本块
angr — Analysis and Coordination — angr 9.0.10689 documentation
https://xz.aliyun.com/t/3990
https://www.cnblogs.com/61355ing/p/10523147.html
angr Tutorials EP1 - Reverse Engineering 101 - YouTube
angr
关于Faster的那些事… (myts2.cn)
[原创]符号执行在自动化Pwn中的简单利用-Pwn-看雪论坛-安全社区|安全招聘|bbs.pediy.com
shellphish/driller: Driller: augmenting AFL with symbolic execution! (github.com)