一、利用cred结构体提权:
1.前置知识:
(1)kernel中会为每个进程创建一个cred结构体,保存了该进程的权限等信息如(uid,gid)等,如果能修改这个结构体那么就修改了这个进程的权限。
(2)修改进程的权限为root之后,再通过该进程开的shell那么也就是root权限了,实现提权。
2.利用手段:
(1)通过UAF,将一块已经释放的堆块修改大小为cred结构体大小,然后创建进程,就会将该堆块申请为cred结构体。
(2)再通过UAF将该cred结构体中的uid、gid改掉,实现进程提权。
▲那么如何知道cred结构体的大小呢,不同linux内核版本的cred结构体大小不同:
①通过linux内核版本,上源码查看网址,查找对应的cred结构体:
访问对应版本:https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.4.70/source/include/linux/cred.h
可以看到某内核的cred结构体大小,这里是0xa8:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 //注释头 struct cred { atomic_t usage; 0x4 #ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_CREDENTIALS debug选项去掉 atomic_t subscribers; /* number of processes subscribed */ void *put_addr; unsigned magic; #define CRED_MAGIC 0x43736564 #define CRED_MAGIC_DEAD 0x44656144 #endif kuid_t uid; /* real UID of the task */ 0x4 kgid_t gid; /* real GID of the task */ 0x4 kuid_t suid; /* saved UID of the task */ 0x4 kgid_t sgid; /* saved GID of the task */ 0x4 kuid_t euid; /* effective UID of the task */ 0x4 kgid_t egid; /* effective GID of the task */ 0x4 kuid_t fsuid; /* UID for VFS ops */ 0x4 kgid_t fsgid; /* GID for VFS ops */ 0x4 unsigned securebits; /* SUID-less security management */ 0x4 kernel_cap_t cap_inheritable; /* caps our children can inherit */ 0x8 kernel_cap_t cap_permitted; /* caps we're permitted */ 0x8 kernel_cap_t cap_effective; /* caps we can actually use */ 0x8 kernel_cap_t cap_bset; /* capability bounding set */ 0x8 kernel_cap_t cap_ambient; /* Ambient capability set */ 0x8 #ifdef CONFIG_KEYS unsigned char jit_keyring; /* default keyring to attach requested 0x8 * keys to */ struct key __rcu *session_keyring; /* keyring inherited over fork */ 0x8 struct key *process_keyring; /* keyring private to this process */ 0x8 struct key *thread_keyring; /* keyring private to this thread */ 0x8 struct key *request_key_auth; /* assumed request_key authority */ 0x8 #endif #ifdef CONFIG_SECURITY void *security; /* subjective LSM security */ 0x8 #endif struct user_struct *user; /* real user ID subscription */ 0x8 struct user_namespace *user_ns; /* user_ns the caps and keyrings are relative to. */ 0x8 struct group_info *group_info; /* supplementary groups for euid/fsgid */ 0x8 struct rcu_head rcu; /* RCU deletion hook */ 0x10 };
这里大小是去掉debug部分的成员的大小,因为题目给的bzImage内核文件一般都不包含debug选项,包含的话会特别大,这里后面标注的大小是某个大佬标注:
https://www.jianshu.com/p/a465b3f6d7cb
②直接自己写一个小module加载打印cred结构体大小:
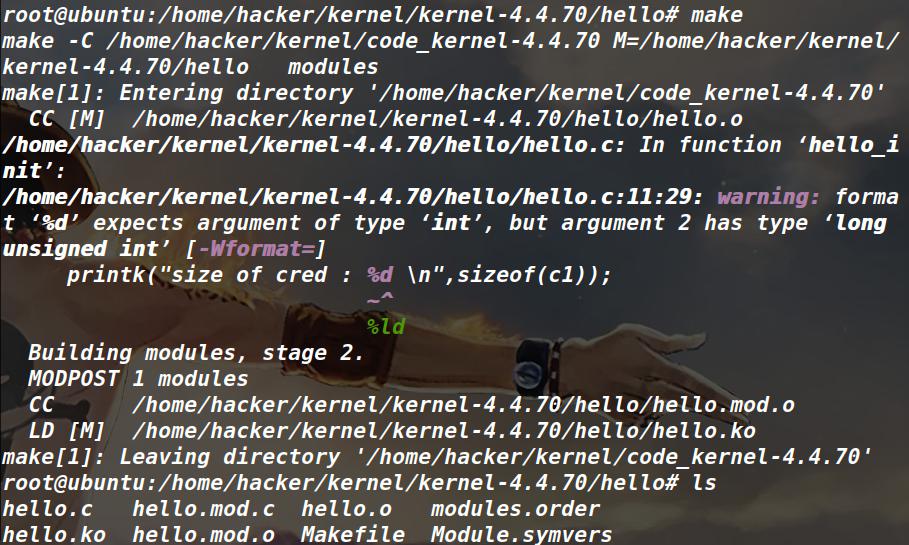
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 //简单modules #include <linux/init.h> #include <linux/module.h> #include <linux/kernel.h> #include <linux/cred.h> MODULE_LICENSE("Dual BSD/GPL"); struct cred c1; static int hello_init(void) { printk("<1> Hello world!\n"); printk("size of cred : %d \n",sizeof(c1)); return 0; } static void hello_exit(void) { printk("<1> Bye, cruel world\n"); } module_init(hello_init); module_exit(hello_exit);
A.新建一个hello文件夹,放上述代码hello.c和Makefile,设置Makefile为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 obj-m := hello.o KERNELDR := /usr/src/linux-headers-4.15.0-22-generic PWD := $(shell pwd) modules: $(MAKE) -C $(KERNELDR) M=$(PWD) modules moduels_install: $(MAKE) -C $(KERNELDR) M=$(PWD) modules_install clean: rm -rf *.o *~ core .depend .*.cmd *.ko *.mod.c .tmp_versions
这里的KERNELDR目录是编译之后的kernel目录
make命令编译下这个hello.c,会生成几个文件,只需要hello.ko
B.在根文件系统中vim init,设置一下,加上insmod /hello.ko,再重新打包,通过qemu启动内核,启动命令为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 #注释头 qemu-system-x86_64 \ -m 128M \ -kernel ./bzImage \ -initrd ./rootfs.cpio \ -append "root=/dev/ram rw console=ttyS0 oops=panic panic=1 kaslr" \ -netdev user,id=t0, -device e1000,netdev=t0,id=nic0 \ -nographic \
这里不能在append中添加quiet命令,否则没法打印出来
C.之后就可以看到
参照:https://ch4r1l3.github.io/2018/10/07/linux-kernel-pwn-%E5%88%9D%E6%8E%A2-1/
(3)一般而言,修改cred结构体可以直接从头开始,将头部至gid的部分都赋值为0即可,因为前面的数据基本用不到,不需要再去找原始数据来赋值。
二、利用ptmx设备中的tty_struct结构体
1.前置知识:
(1)打开设备,open(“/dev/ptmx”, O_RDWR)时会创建一个tty_struct
(2)tty_struct结构体中有一个const struct tty_operations *ops;结构体指针,偏移为xx。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 //注释头 struct tty_struct { int magic; struct kref kref; struct device *dev; struct tty_driver *driver; const struct tty_operations *ops; int index; /* Protects ldisc changes: Lock tty not pty */ struct ld_semaphore ldisc_sem; struct tty_ldisc *ldisc; struct mutex atomic_write_lock; struct mutex legacy_mutex; struct mutex throttle_mutex; struct rw_semaphore termios_rwsem; struct mutex winsize_mutex; spinlock_t ctrl_lock; spinlock_t flow_lock; /* Termios values are protected by the termios rwsem */ struct ktermios termios, termios_locked; struct termiox *termiox; /* May be NULL for unsupported */ char name[64]; struct pid *pgrp; /* Protected by ctrl lock */ struct pid *session; unsigned long flags; int count; struct winsize winsize; /* winsize_mutex */ unsigned long stopped:1, /* flow_lock */ flow_stopped:1, unused:BITS_PER_LONG - 2; int hw_stopped; unsigned long ctrl_status:8, /* ctrl_lock */ packet:1, unused_ctrl:BITS_PER_LONG - 9; unsigned int receive_room; /* Bytes free for queue */ int flow_change; struct tty_struct *link; struct fasync_struct *fasync; int alt_speed; /* For magic substitution of 38400 bps */ wait_queue_head_t write_wait; wait_queue_head_t read_wait; struct work_struct hangup_work; void *disc_data; void *driver_data; struct list_head tty_files; #define N_TTY_BUF_SIZE 4096 int closing; unsigned char *write_buf; int write_cnt; /* If the tty has a pending do_SAK, queue it here - akpm */ struct work_struct SAK_work; struct tty_port *port; };
结构体大小为0x2e0,但是不知道各个版本的大小是不是都一样,如果需要查看大小,仍然可以用上述方法,去网站,或者编译一个小module
网站:https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.4.72/source/include/linux/tty.h
module:参照上面的,打印即可。
(3)tty_operations结构体中有一个int (*write)(struct tty_struct * tty,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 //注释头 struct tty_operations { struct tty_struct * (*lookup)(struct tty_driver *driver, struct inode *inode, int idx); int (*install)(struct tty_driver *driver, struct tty_struct *tty); void (*remove)(struct tty_driver *driver, struct tty_struct *tty); int (*open)(struct tty_struct * tty, struct file * filp); void (*close)(struct tty_struct * tty, struct file * filp); void (*shutdown)(struct tty_struct *tty); void (*cleanup)(struct tty_struct *tty); int (*write)(struct tty_struct * tty, const unsigned char *buf, int count); int (*put_char)(struct tty_struct *tty, unsigned char ch); void (*flush_chars)(struct tty_struct *tty); int (*write_room)(struct tty_struct *tty); int (*chars_in_buffer)(struct tty_struct *tty); int (*ioctl)(struct tty_struct *tty, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg); long (*compat_ioctl)(struct tty_struct *tty, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg); void (*set_termios)(struct tty_struct *tty, struct ktermios * old); void (*throttle)(struct tty_struct * tty); void (*unthrottle)(struct tty_struct * tty); void (*stop)(struct tty_struct *tty); void (*start)(struct tty_struct *tty); void (*hangup)(struct tty_struct *tty); int (*break_ctl)(struct tty_struct *tty, int state); void (*flush_buffer)(struct tty_struct *tty); void (*set_ldisc)(struct tty_struct *tty); void (*wait_until_sent)(struct tty_struct *tty, int timeout); void (*send_xchar)(struct tty_struct *tty, char ch); int (*tiocmget)(struct tty_struct *tty); int (*tiocmset)(struct tty_struct *tty, unsigned int set, unsigned int clear); int (*resize)(struct tty_struct *tty, struct winsize *ws); int (*set_termiox)(struct tty_struct *tty, struct termiox *tnew); int (*get_icount)(struct tty_struct *tty, struct serial_icounter_struct *icount); #ifdef CONFIG_CONSOLE_POLL int (*poll_init)(struct tty_driver *driver, int line, char *options); int (*poll_get_char)(struct tty_driver *driver, int line); void (*poll_put_char)(struct tty_driver *driver, int line, char ch); #endif const struct file_operations *proc_fops; };
这个结构体在伪造的时候就可以随便伪造了,只要函数偏移位置对就行。
(4)所以我们伪造一个tty_struct结构体fake_tty_1,利用UAF漏洞将一个堆块申请为这个结构体,修改其const struct tty_operations *ops;结构体指针指向另一个伪造的tty_operations结构体fake_tty_2。
(5)将tty_operations结构体fake_tty_2中的int (*write)(struct tty_struct * tty,
(6)控制程序之后一般需要关闭掉smep保护,之后用ret2Usr来提权。
▲关闭smep保护:
需要将CR4寄存器中的第20位置0,即可关闭。一般在ROP链中执行下列gadget即可:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 #注释头 mov cr4,0x6f0; ret; ---------------------------------------------------------------------- pop rdi; ret 0x6f0 mov cr4,rdi; ret;
上面两种都行,或者其它满足条件的gadget也可以,这里0x6f0是想绕过一些机制。
2.利用手段:
(1)通过UAF申请得到tty_struct结构体指针,修改const struct tty_operations *ops使其指向用户空间伪造的tty_operations结构体,伪造的tty_operations结构体中的write指针指向ROP链。
(2)ROP链进行迁移内核栈,关闭smep保护,正常ret2Usr。